Table of Contents
Prokaryotic Cell
Prokaryotic cells are single-celled microorganisms known to be the earliest on earth. Prokaryotes include Bacteria and Archaea. The photosynthetic prokaryotes include cyanobacteria that perform photosynthesis.
A prokaryotic cell consists of a single membrane & therefore, all the reactions occur within the cytoplasm.
Prokaryotic Cell Diagram
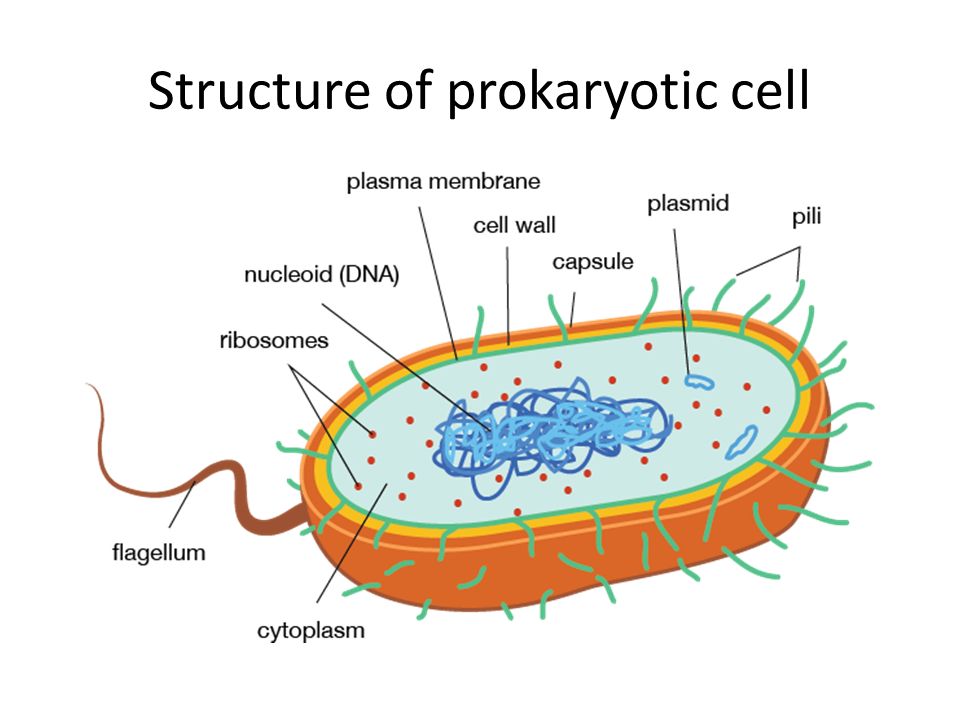
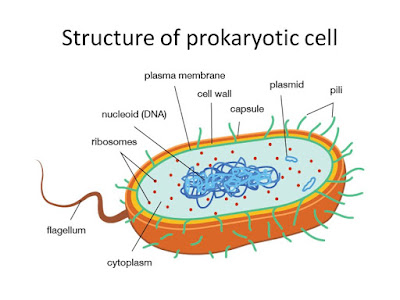
Prokaryotic cell structure
A prokaryotic cell does not have a nuclear membrane. However, the genetic material is present in a region in the cytoplasm known as nucleoid. They may be spherical, rod-shaped, or spiral. A prokaryotic cell structure is as follows:
1. Capsule :- It is an outer protective covering found in the bacterial cells, in addition to the cell wall. It helps in moisture retention, protects the cell when engulfed, and helps in the attachment of cells to nutrients and surfaces.
2. Cell Membrane :- The cell membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space) which protects the cell from its environment.
3. Cell Wall :- A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism.
4. Pili :- These are hair-like outgrowths that attach to the surface of other bacterial cells. Pili are similar structures that can serve many functions, including helping the bacterium move or helping it transfer DNA to another bacterium.
5. Flagella :- These are long structures in the form of a whip, that help in the locomotion of a cell.
6. Cytoplasm :- It is a thick solution that fills each cell and is enclosed by the cell membrane. It is mainly composed of water, salts, and proteins. In eukaryotic cells, the cytoplasm includes all of the material inside the cell and outside of the nucleus.
7. Ribosomes :- These are involved in protein synthesis. Which are essentially little protein factories, can be found scattered throughout the cytoplasm.
8. Plasmids :- Plasmids are non-chromosomal DNA structures. These are not involved in reproduction. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules.
9. Nucleoid :- It is the region in the cytoplasm where the genetic material is present.
Eukaryotic cell
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane and form large and complex organisms. Organisms based on the eukaryotic cell include protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals. They are classified under the kingdom Eukaryota.
They can maintain different environments in a single cell that allows them to carry out various metabolic reactions. This helps them grow many times larger than the prokaryotic cells.
Eukaryotic cell diagram
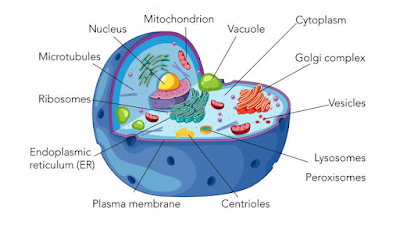
Eukaryotic cell structure
1. Nucleus :- The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle that contains genetic material (DNA) of eukaryotic organisms.
2. Nucleolus :- The nucleolus is a round body located inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. It is not surrounded by a membrane but sits in the nucleus. The nucleolus makes ribosomal subunits from proteins and ribosomal RNA, also known as rRNA.
3. Ribosomes :- Ribosomes are minute particles consisting of RNA and associated proteins that function to synthesize proteins. Proteins are needed for many cellular functions such as repairing damage or directing chemical processes. Ribosomes can be found floating within the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum.
4. Mitochondria :- These are also known as “powerhouse of cells” because they produce energy.
It consists of an outer membrane and an inner membrane. The inner membrane is divided into folds called cristae.
They help in the regulation of cell metabolism.
5. Endoplasmic reticulum:- It is a network of small, tubular structures that divides the cell surface into two parts: luminal and extraluminal.
Endoplasmic Reticulum is of two types:
- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum contains ribosomes.
- Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum that lacks ribosomes and is therefore smooth.
6. Golgi apparatus :- It is named after the scientist who discovered it, Camillo Golgi. Golgi is made of many flat, disc-shaped structures called cisternae. It is present in all eukaryotic cells except human red blood cells and sieve cells of plants.
7. Plastids :- They are double membrane organelles found in plant cells. They contain pigments and are of three types:
- Chloroplast that contains chlorophyll and is involved in photosynthesis.
- Chromoplast that contains a pigment called carotene that provides the plants yellow, red, or orange colours.
- Leucoplasts that are colourless and store oil, fats, carbohydrates, or proteins.
8. Plasma Membrane :-
- The plasma membrane separates the cell from the outside environment.
- It comprises specific embedded proteins, which help in the exchange of substances in and out of the cell.




Leave a Reply