Production | Methods, Factors, and Importance
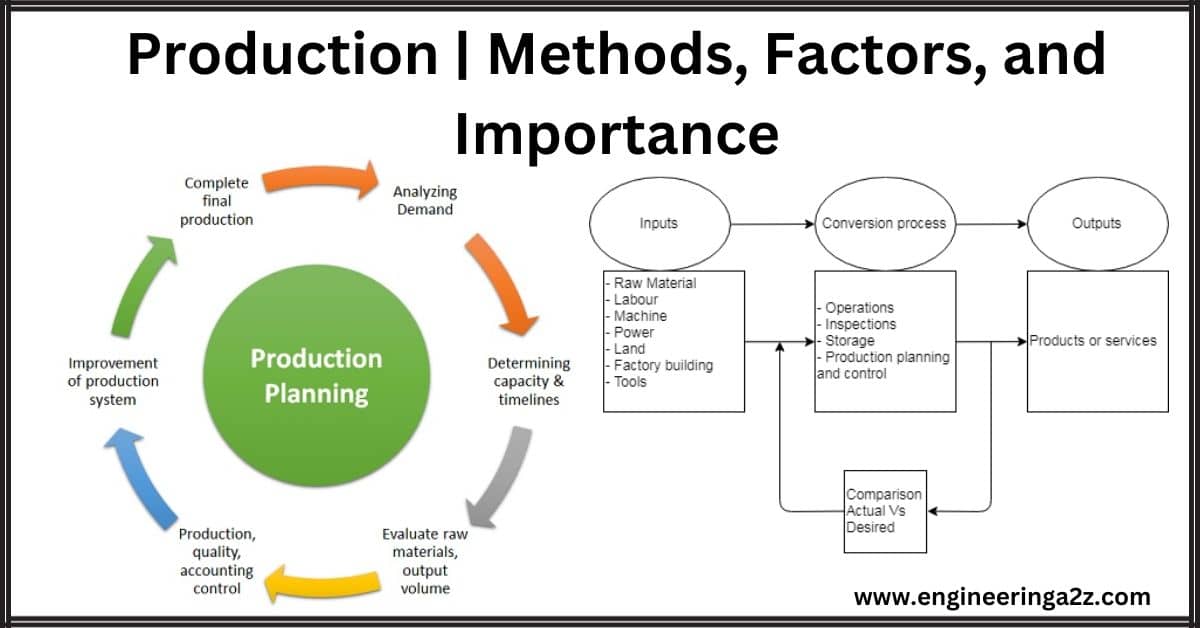
Introduction In economics, the term "production" doesn't refer to the creation of physical goods, but rather to the process of enhancing the utility or value of existing resources. This concept…
Macro Economics | Scope, Uses, and Limitations
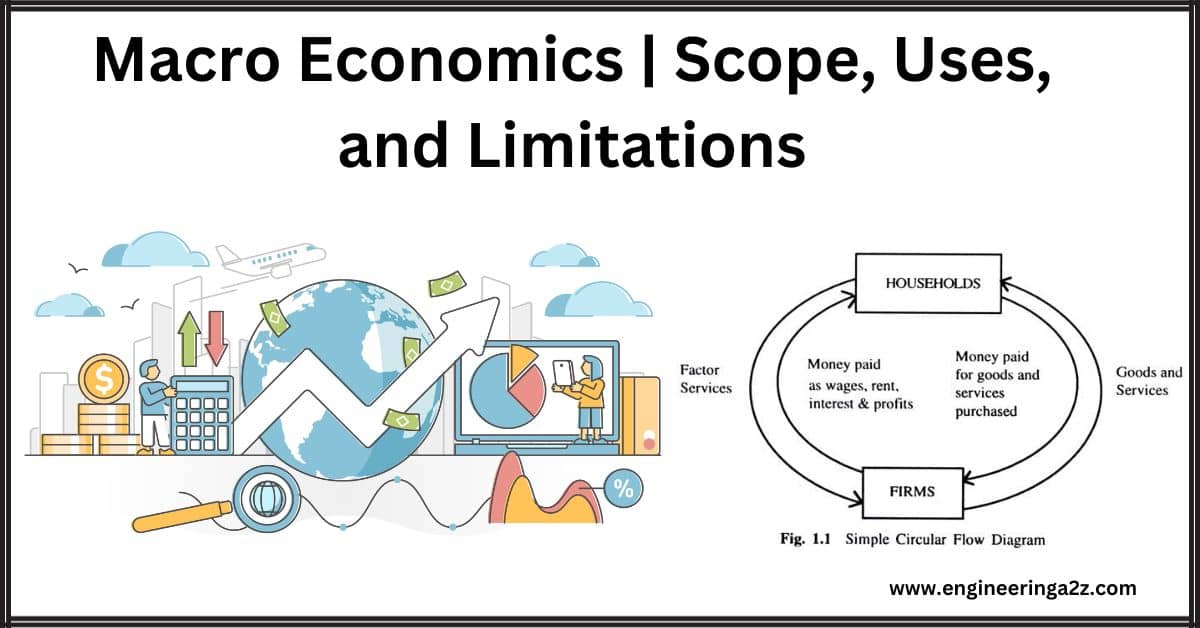
'Macro' as used in the English language originates in the Greek word Makros, meaning large. Hence, in macroeconomics, economic problems are studied from the point of view of the entire…
Entrepreneur | Functions, Qualities, Efficiency, and Importance
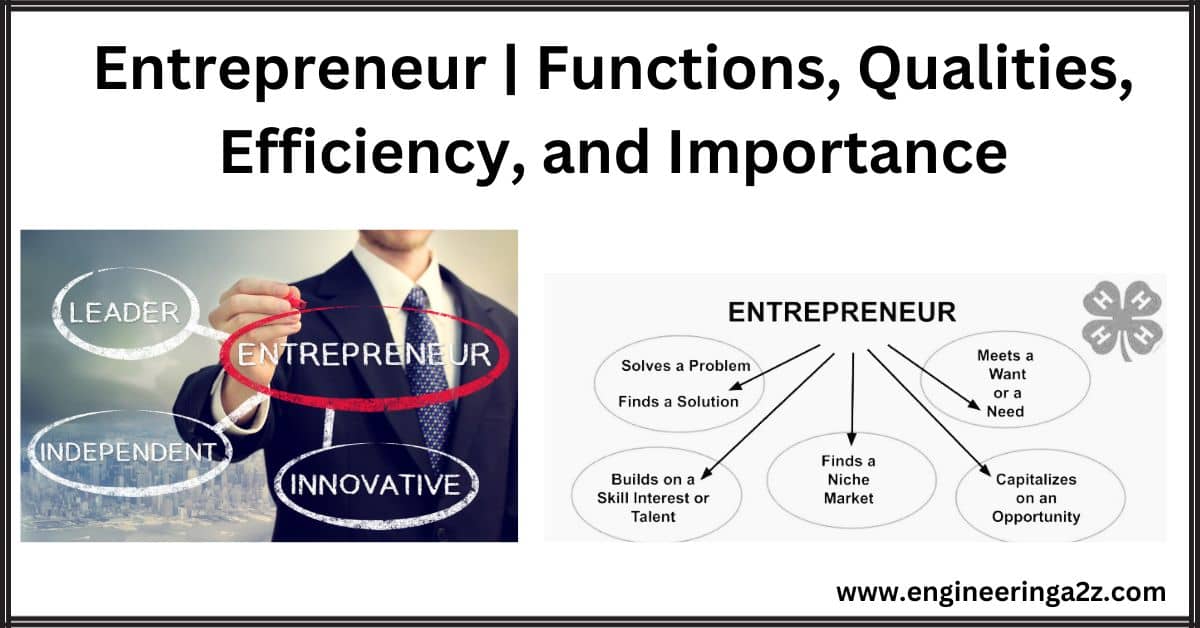
Entrepreneur In the modern age, the significance of the entrepreneur as a factor of production has increased manifold. An entrepreneur is a chief human factor of production. Classical economists made…
Division of Labour | Main Forms, Advantages, and Favourable Conditions
Introduction Adam Smith came up with the idea that people should do what they're best at. For instance, a cook should cook, and a professor should teach. This way, everyone…
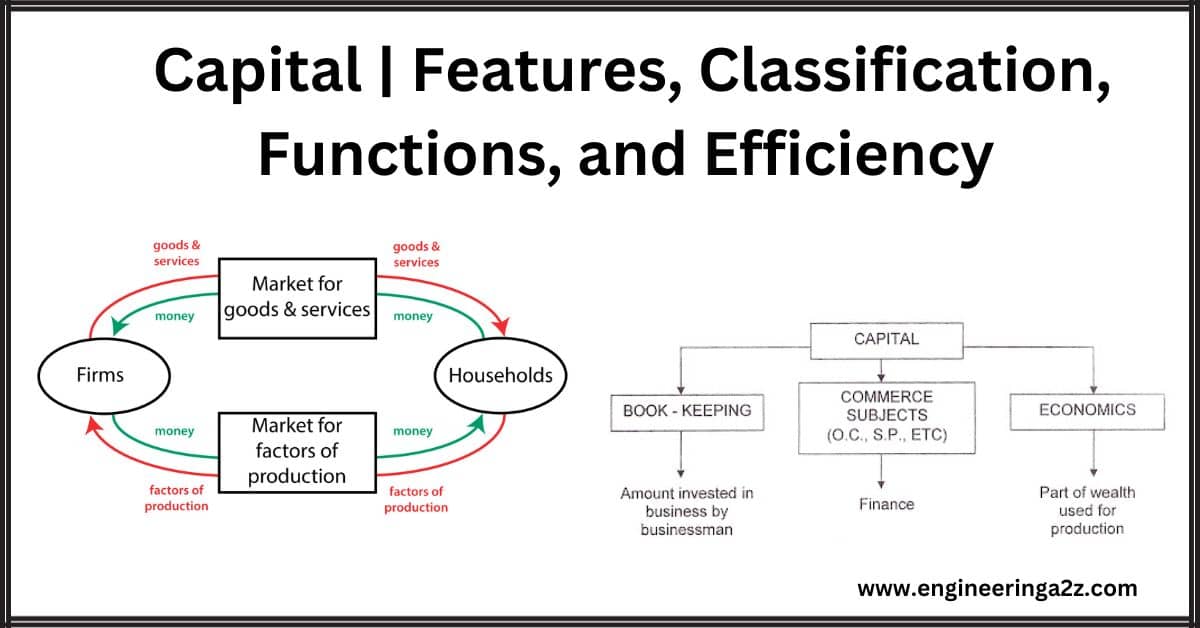
Capital | Features, Classification, Functions, and Efficiency
Capital Capital is a crucial factor in production. In everyday language, we often use terms like wealth, capital, and money interchangeably. However, in economics, capital refers to the portion of…
Financial management | Types, Objectives, Functions and Career
Definition Financial management is like being the money boss of a business. Whether it's a small shop or a big company, someone has to handle all the cash stuff. This…
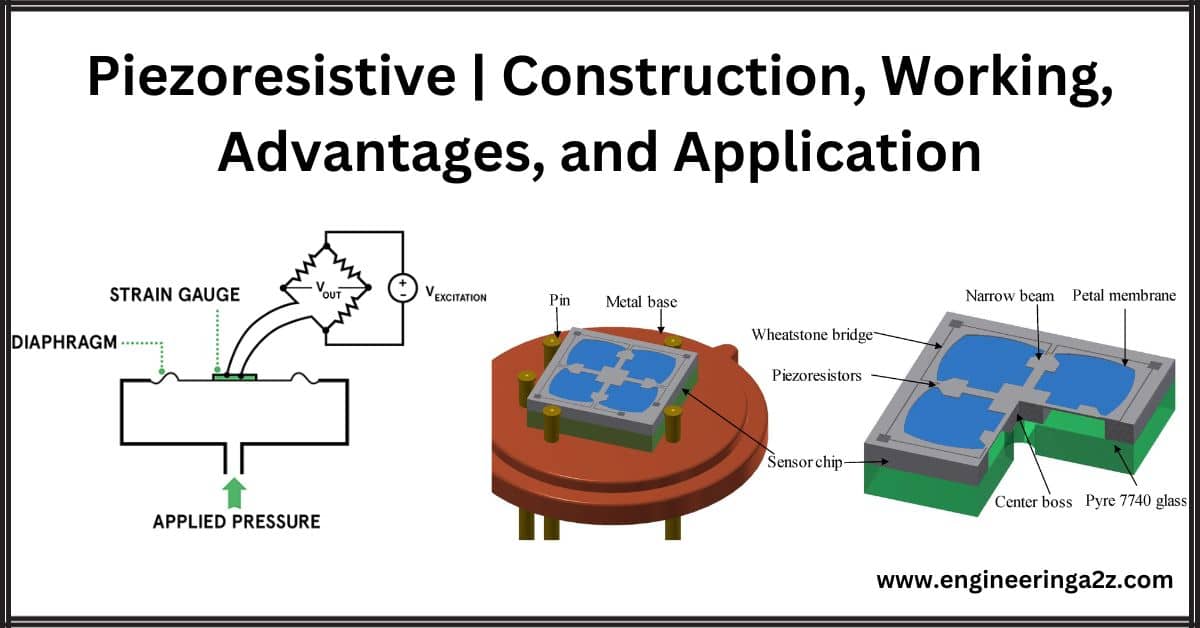
Piezoresistive | Construction, Working, Advantages, and Application
Piezoresistive Piezoresistive materials are substances that exhibit changes in electrical resistance when subjected to mechanical stress or strain. This property makes them particularly useful in sensor applications for measuring pressure,…
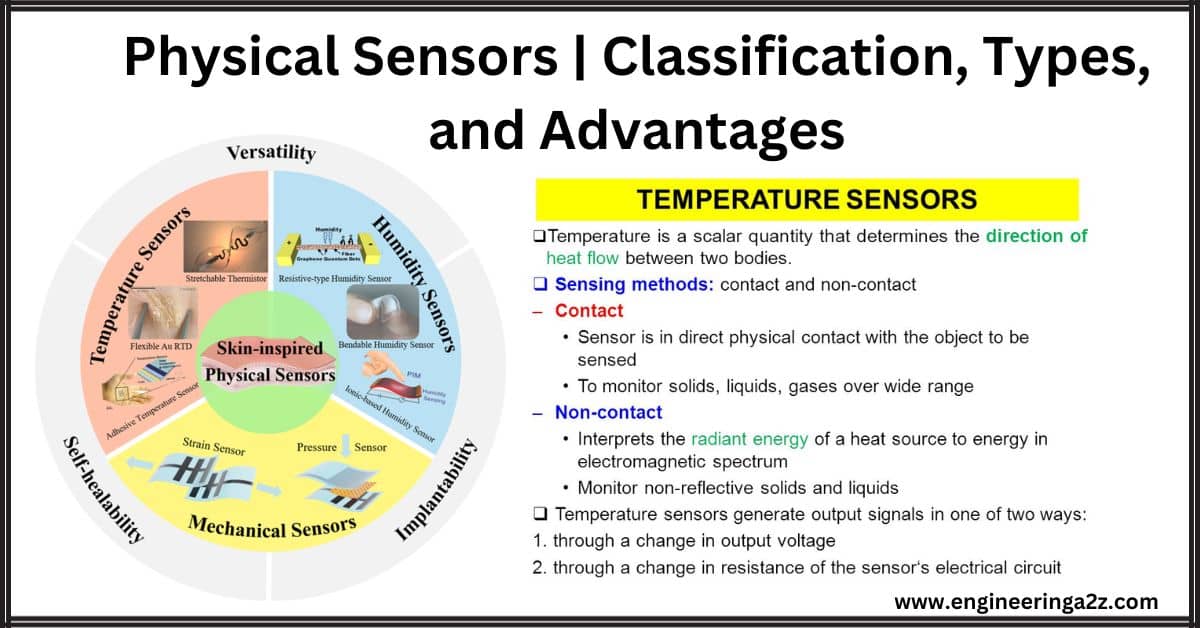
Physical Sensors | Classification, Types, and Advantages
Introduction Physical sensors are devices that detect and respond to physical input from the environment. They convert various types of physical quantities, such as light, temperature, pressure, motion, or proximity,…
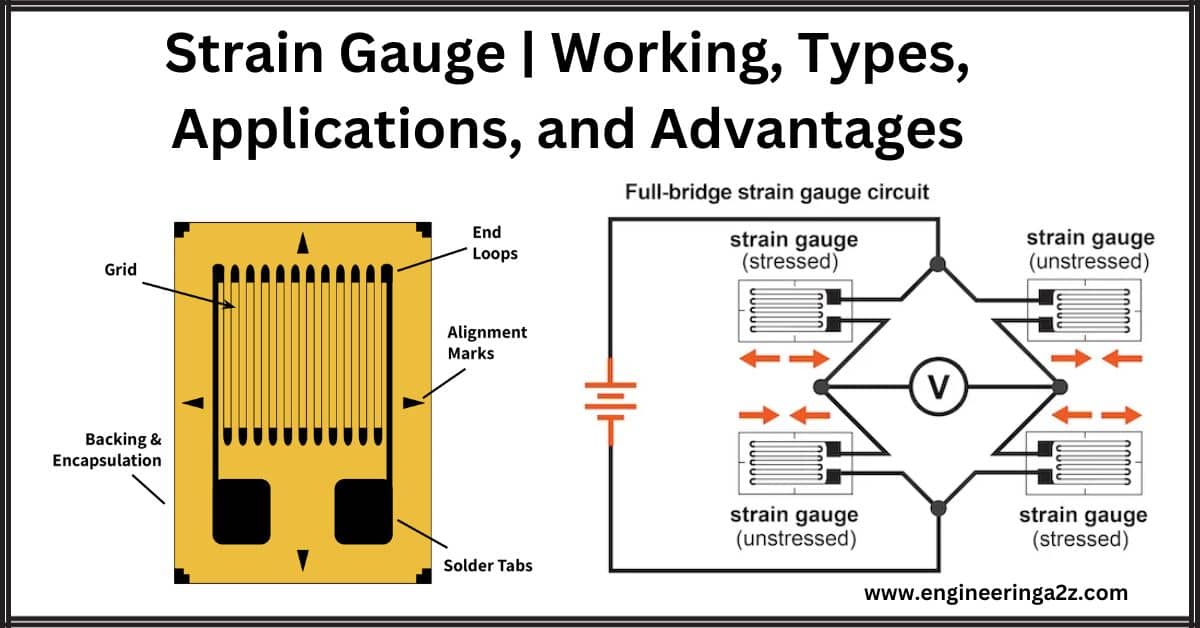
Strain Gauge | Working | Types | Applications and Advantages
Introduction A strain gauge is like a smart sensor that senses changes in resistance when you apply force, pressure, tension, or weight. It helps convert these physical forces into electrical…
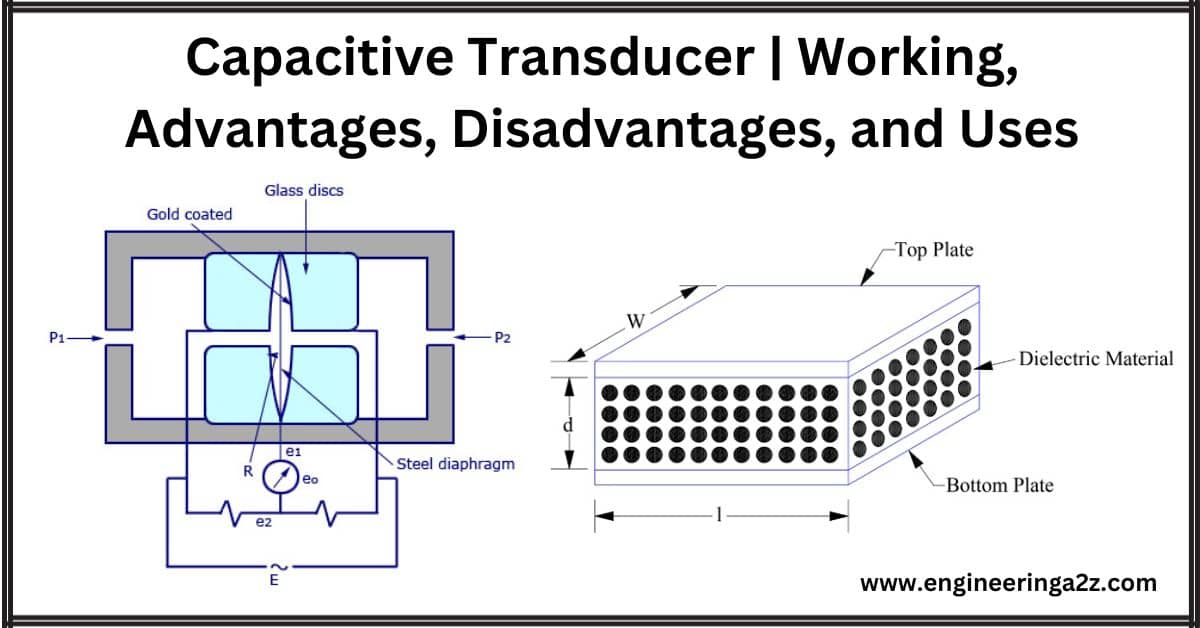
Capacitive Transducer | Working | Advantages | Disadvantages and Uses
Introduction A capacitive transducer is a device used to measure displacement and pressure. It relies on changes in capacitance, which is a measure of how much electric charge a device…