
Table of Contents
Definition
Financial management is like being the money boss of a business. Whether it’s a small shop or a big company, someone has to handle all the cash stuff. This means making sure money comes in (from selling things or providing services), paying the bills, keeping track of everything, and following the rules set by the government.
In smaller businesses, there might be one person, like an accountant, who works with the bank to handle these money moves. But in big companies, it gets more complicated. They have a whole team of money experts led by someone important, like the Chief Financial Officer (CFO) or Finance Head.
This money team’s main job is to keep the company’s finances healthy. That means ensuring there’s always enough money to keep things going smoothly. But they do more than that. They also handle things like loans, and debts, keeping track of what the company owns and owes, making intelligent investments, and even getting more money from investors or selling company shares.
So, in simple terms, the money team protects the company’s cash, keeps an eye on all the money stuff, and tries to make the company as profitable as possible.
Types Of Financial Management
Financial management can be broken down into three main types or functions:
- Capital Budgeting: This is all about figuring out what financial moves a company needs to make to achieve its short-term and long-term goals. It involves deciding where to invest capital funds to support the company’s growth and development.
- Capital Structure: Here, the focus is on determining how the company should finance its operations and growth. It involves deciding whether to use debt (borrowing the money), seeking investments from private equity firms, selling assets like real estate, or selling company ownership through equity shares.
- Working Capital Management: This function ensures that the company always has enough cash for its everyday operations, such as paying employees and buying materials for production. It’s about managing the day-to-day finances to keep the business running smoothly.
Objectives of Financial Management
Financial managers have important goals to achieve to keep a company running smoothly:
- Figuring out how much money is needed: Financial managers have to figure out how much money the company needs for things like buying stuff, advertising, having some extra money just in case, and paying employees in the long run. Successful companies have clear plans for how much money they’ll need in the short and long term.
- Deciding where the money comes from: They also decide where the money should come from, like if the company should borrow money or use its own savings. This is important for both short-term and long-term plans.
- Making smart money rules: Financial managers create rules about how the company handles its cash when to borrow, and when to lend money, among other things.
- Using resources wisely: The best financial managers know how to use the company’s money in the smartest way possible. This means spending less when needed and making more money in return. It’s like turning cash into even more cash to make the company as successful as possible.
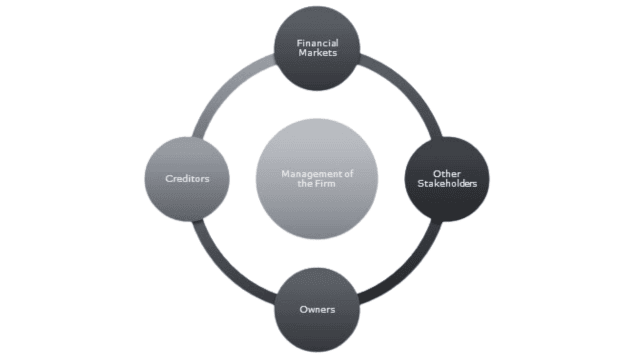
Functions of Financial Managers and Advisors
Financial managers and advisors have important jobs to do to make sure a company does well:
- Getting Money: They make sure the company has enough money to grow and do well. They can get this money by either borrowing it or by selling part of the company to investors. They have to be smart about how much they borrow and how much of the company they give away.
- Spending Money Wisely: It’s not just about getting money; they also have to be really careful about how they spend it. They need to decide where to use the funds based on things like how big the company is, how much it wants to grow, and whether it’s spending on short-term or long-term things.
- Planning for Profits: Making money is a big goal for any business. The profits a company makes show how well it’s doing financially. Financial managers decide what to do with these profits. Should they use them to buy more stuff, expand the business, or save them for a rainy day? It’s a big decision.
- Understanding the Stock Market: If a company’s shares are traded on the stock market, it means people can buy and sell them. Financial managers need to know how this works and how it affects the company’s value. They also decide whether to give some of the profits to the shareholders or reinvest the money in the business, which can make the shareholders happy or upset.
Career Opportunities in Financial Management
There are many great career options in the field of financial management, and I’ll break down some of the key ones for you:
- Corporate Finance: These professionals help businesses get the money they need to run smoothly. They also make important decisions about where to invest that money to make the company more profitable. It’s about balancing risks and profits, analyzing industry trends, and finding ways to improve the company’s financial health.
- Investment Banking: This is a prestigious career where experts help companies make big financial decisions, like mergers or acquisitions. They use data and economic trends to guide these decisions. There are also roles in trading stocks and managing investments. To succeed here, you need a deep understanding of financial markets and economics.
- Portfolio Management: Portfolio managers make strategic decisions about how a company should invest its money. They analyze markets and focus on factors like growth and safety to make smart choices. This role requires a mix of math, business knowledge, and data analysis.
- Risk Management: In a world with ever-changing markets and various risks, risk managers are crucial. They use their math skills and market knowledge to help clients make safe financial choices. There are different types of risk management roles, like financial risk management, enterprise risk management, and more. These roles can be well-paying and are found in industries like insurance and finance.
- Financial Planning: Financial planners are in high demand, helping individuals and companies manage their money wisely. They analyze financial statements, income, and expenses to create customized financial plans. You can work as an independent financial planner, start your own financial planning business, or work for companies in finance and wealth management.
- Commercial Banking: Banks are essential in our financial lives, offering services like savings and current accounts, loans, and credit cards. Careers in commercial banking are respected, well-paying, and offer stable working hours. Having tech skills along with a finance degree can make you highly employable in this field.
- Compliance and Internal Financial Management: Companies hire professionals to ensure they follow laws, ethical standards, and industry regulations. These roles are suitable for people with degrees in accounting and law. Specialized qualifications like a diploma in financial accounting can open doors to internships and jobs in this area.
To prepare for these careers, you may consider pursuing relevant qualifications like a finance degree, a diploma in banking and finance, or a financial risk management course. These qualifications can help you stand out in the competitive world of financial management.
Importance of Financial Management
Financial management is of paramount importance in any organization, regardless of its size or industry. Here are some key reasons why financial management is crucial:
- Sustainability and Survival: Effective financial management ensures the long-term survival and sustainability of a business. It helps companies avoid financial crises and bankruptcy by ensuring there’s enough cash to cover day-to-day operations and to invest in growth.
- Strategic Decision-Making: Financial management provides the data and analysis needed for making informed strategic decisions. It helps businesses identify profitable opportunities, assess risks, and allocate resources wisely.
- Resource Allocation: Financial management guides the allocation of financial resources to different business areas. It helps determine which projects or investments are the most lucrative and align with the company’s objectives.
- Risk Mitigation: Managing financial risks is essential in today’s volatile business environment. Financial management helps identify, assess, and mitigate risks related to investments, market fluctuations, and financial obligations.
- Efficient Operations: It ensures the efficient use of resources. By monitoring cash flows, expenses, and revenue, financial managers can identify inefficiencies and implement cost-saving measures.
- Compliance and Legal Obligations: Businesses must adhere to various financial regulations and tax laws. Effective financial management helps ensure compliance, reducing the risk of legal issues and financial penalties.
- Investor Confidence: Investors and stakeholders, including shareholders and lenders, rely on accurate financial information to make decisions. Strong financial management builds trust and confidence, attracting potential investors and creditors.
- Creditworthiness: Maintaining a healthy financial position enhances a company’s creditworthiness. This can lead to better borrowing terms and lower interest rates, reducing financing costs.
- Profit Maximization: Financial management aims to optimize profits by managing costs, pricing strategies, and revenue streams effectively.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Sound financial management enables businesses to adapt to changing market conditions, economic cycles, and unexpected events. It provides a financial cushion for emergencies and unforeseen challenges.
- Strategic Planning: Financial management supports strategic planning by aligning financial goals with overall business objectives. It helps set targets, monitor progress, and adjust strategies as needed.
- Investment Decisions: Financial managers play a crucial role in evaluating potential investments, whether in new technology, acquisitions, or market expansion. They assess the expected returns and risks associated with these investments.
- Cash Flow Management: Maintaining healthy cash flow is essential for meeting short-term obligations and seizing opportunities. Effective financial management ensures that cash is available when needed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the primary goal of financial management?
The primary goal of financial management is to maximize shareholder wealth by making effective financial decisions that increase the long-term value of the company.
What are financial management strategies?
A finance strategy is like a plan that combines smart money planning. It makes sure a company’s money, expenses, and budget match its mission and goals.
Is financial management a good career?
Financial management is a top-paying job worldwide. Financial managers work in various areas like stock markets, insurance, and non-bank finance. They often work for banks, insurance firms, or wealthy individuals.
What are the 5 roles of financial management?
The five roles of financial management are planning for financial goals, deciding on long-term investments, managing debt and equity financing, handling short-term cash flow, and mitigating financial risks.
Read Also:
- Energy Management | Need and Environmental Aspects
- Marketing Management | Objectives & Functions of Marketing Management
- Management | Process & Functions of Management
- Quality Systems | Types, Benefits, and Need For Standardization




Leave a Reply