Table of Contents
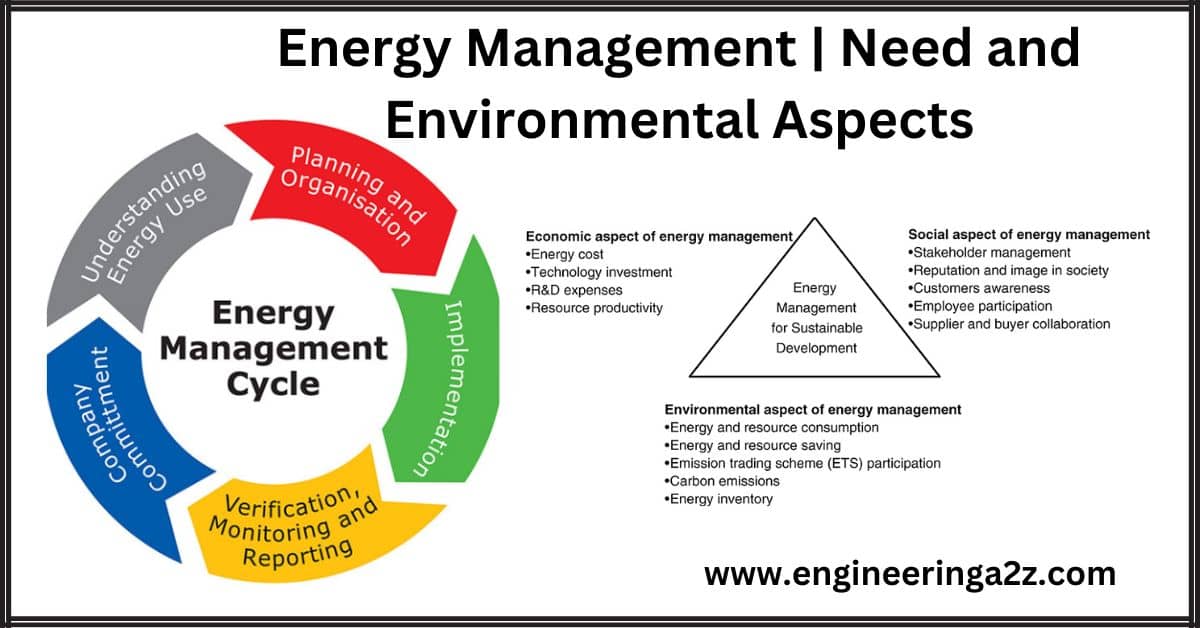
Energy Management
The term energy management refers to the saving of energy. This notably means improving the efficiency of powered devices such as electrical equipment or vehicles and the development of renewable energies. Energy Management is often referred to as demand management. Energy demand management usually implies actions that affect the quantity of energy consumed by users. It also includes actions targeting the reduction of peak demand during periods when energy supply systems are constrained.
Need for Energy Conservation
Energy plays an important role in our day-to-day life. We need the energy to accomplish our work. Nothing is possible without energy. In today’s scenario, energy demand is at its peak. To live a luxurious life, energy demand rises: Energy demand rises due to the technology development. Nowadays, everything depends entirely on technology. Microwave ovens to cook food, washing machines to wash clothes, vehicles for transportation, etc. are technological advancement equipment and require energy to operate. The ability to do work is called energy. It can neither be created nor be destroyed but it can be transformed from one form to another. Heat energy, light energy, wind energy, nuclear energy, mechanical energy, etc. are examples of energy.
Electricity flowing to light a bulb converts electric energy to light energy. The earth provides enough to satisfy every man’s needs but not every man’s. Hard facts on why energy conservation is a must are outlined below:
- We use energy faster than it can be produced: Coal, oil, and natural gas – the most utilized sources take thousands of years to form.
- Energy resources are limited: India has approximately 1% of the world’s energy resources but it has 16% of the world’s population.
- Most of the energy sources we use cannot be reused and renewed: Non-renewable energy sources constitute 80% of the fuel use. It is said that our energy resources may last only for another 40 years or so.
- We save the country a lot of money when we save energy: About 75 percent of our crude oil needs are met from imports which would cost about Rs. 1,50,000 crore a year.
- We save our money when we save energy: Imagine your savings if your LPG cylinder comes for an extra week or there is a cut in your electricity bills.
- We save our energy when we save energy: When we use fuel wood efficiently, our fuel wood requirements are lower and so is our drudgery for its collection.
- Energy saved is energy generated: When we save one unit of energy, it is equivalent to two units of energy produced.
- Save energy to reduce pollution: Energy production and use account for a large proportion of air pollution and more than 83 percent of greenhouse gas emissions. An old Indian saying describes it this way- The earth, water, and the air are not a gift to us from our parents but a loan from our children. Hence, we need to make energy conservation a habit.
Environmental Aspects
Everything that surrounds us constitutes the environment. It is a well-known fact that “man belongs to the environment and the environment belongs to man.” There is no existence of man without a healthy and balanced environment. Thus, the conservation of the environment is mandatory for man.
However, in the recent past, the environmental balance has been disturbed. It is clear from the fact that available conventional sources of energy (e.g. coal, petroleum, etc.) are being depleted at a much higher rate in comparison to the rate at which they are being produced. This is leading to an imbalance in the available sources of energy. Moreover, this is leading to a severe global fuel crisis.
In addition to the above facts, the burning of fossil fuels is severely polluting the environment which has led to the depletion of the ozone layer in the upper atmosphere. Also, global warming is taking place which will ultimately lead to the flooding of the earth and the destruction of life on the planet.
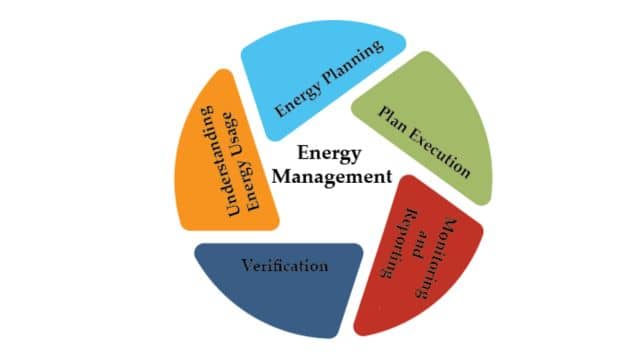
Thus, from an environmental point of view, energy conservation has become a major area of concern. Due to this very fact, non-conventional energy sources are being tapped which will serve the dual purpose of maintaining a regular availability of fossil fuels for a longer duration of time and also the production of pollution-free usable energy. So, energy management also helps to a great extent in saving fossil fuel by decreasing the demand for energy and in turn maintaining environmental balances.
The environmental aspects of energy conservation are as follows:
- Reduced dependence on non-renewable sources of energy: Based on current known reserves and consumption of these fuels, the following amount of each fossil fuel remains available as of 2003: (a) Oil: Approximately 1,000 billion barrels, enough to last 38 years. (b) Natural Gas: Approximately 5,400 trillion cubic feet, enough to last 59 years. (c) Coal: Approximately 1,000 billion metric tons, enough to last 245 years.
- Conservation protects national energy security by reducing our dependence on foreign sources of oil.
- Protects the economy and consumers from possible price fluctuations and from energy service disruptions due to natural disasters or other causes.
- The increasing demand for electricity and natural gas requires your utility to find new supplies of energy. Most new supply options require a great deal of money upfront, which increases your utility bills.
- Studies show that utility or state investment in energy efficiency helps the local economy. Instead of importing natural gas and electricity supply from outside of your community, energy efficiency relies on domestic and local companies and retailers to provide energy management services and energy-saving products.
- Energy efficiency programs provide customers with home improvements that enhance home comfort and increase property values for homeowners and businesses.
- Extracting fossil fuels like coal and oil from underground disturbs and contaminates underground water supplies. This contamination pollutes the water and can render it unsuitable for human or animal consumption.
- The buildings, equipment, and roadways necessary for extracting fossil fuels and producing useable energy are a significant disruption to wildlife and the natural environment. Habitat is diminished at the site of extraction as well as in the areas surrounding roadways and railways erected to transport the raw materials to where they will be processed and used.
- The potential for oil spills is a well-known hazard of our dependence on fossil fuels. By reducing the amount of energy, we consume we are also reducing the amount of oil that must be transported around the world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Define pollution?
The intermixing of contaminants into the natural resources leading to their degradation is k known as Pollution.
-
Define overpopulation?
An increase in the percentage of population day-by-day is termed as over-population.
-
Define global warming?
The increase in the temperature of the earth due to human activities is called global warming.
-
Define natural resource depletion?
The exhaustion of natural resources by overuse is termed a natural resource depletion process.
Read Also:
- Characteristics and Advantages of A.C. Over D.C. and Vice Versa
- DIAC | Construction | Working and V-I Characteristics
- Difference Between A.C. and D.C.
- UPS | Types | Comparison Between Online and Offline UPS
- Stand Alone PV System | Schematics and its Components











Leave a Reply