Table of Contents
Solar Furnace
A solar furnace is an instrument to get high temperatures by concentrating solar radiation onto a specimen. Solar furnaces are used for scientific investigations.
Read Also
Solar Cookers | Working Principle, Construction, and Applications
Working Principle of Solar Furnace
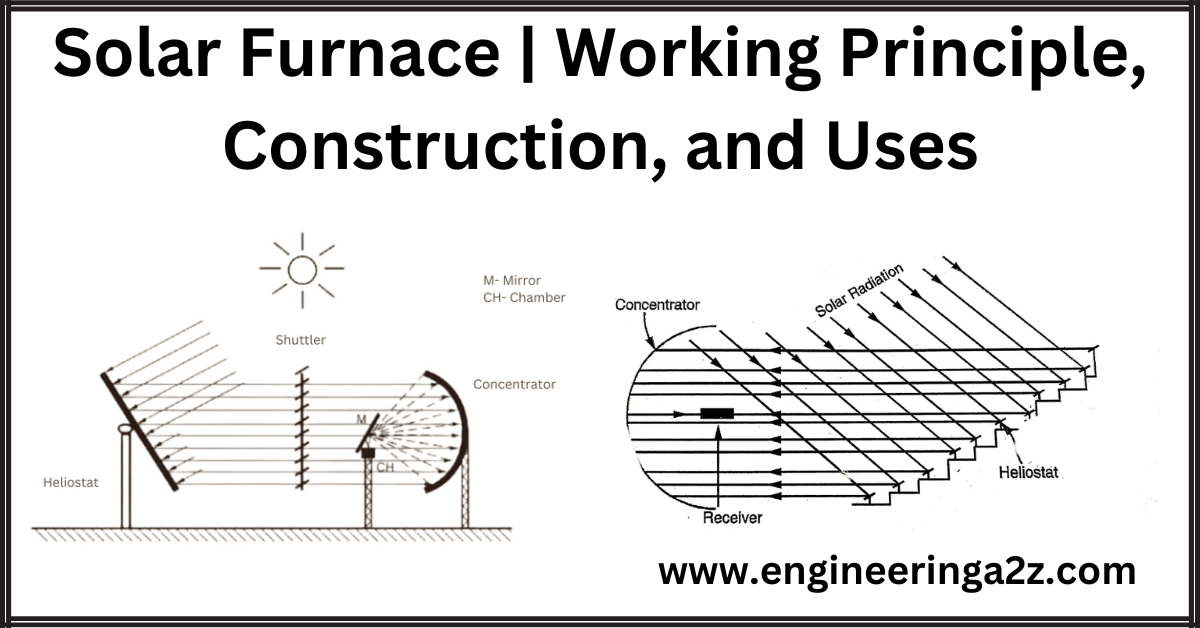
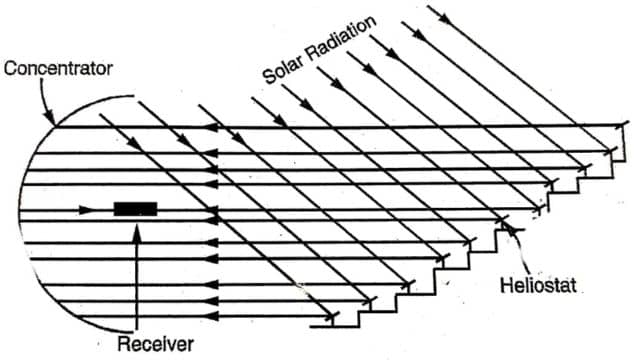
The solar furnace works by using a series of mirrors called heliostats to reflect sunlight onto a large curved mirror. The heliostats are placed on a sloping surface or hillside to ensure that they always reflect sunlight in the same direction, regardless of the sun’s position. The large curved mirror, known as the collector, is made up of fixed mirrors attached to a structure. It focuses the reflected sunlight onto a small area called the receiver.
To make the mirrors for the heliostats, a glass plate is ground and polished until it becomes optically flat. Then, it is coated with aluminum or silver using a vacuum evaporation process and covered with a suitable film.
The heliostats are able to move in two ways: changing their elevation (angle of tilt) and azimuth (horizontal direction). This movement is achieved by rotating the frame of the heliostat using hydraulic or electric driving mechanisms. The rotation is controlled by a servo system or a time system to ensure that the heliostats continuously follow the sun’s movement.
Alternatively, multiple heliostats can be used to redirect sunlight into a concentrator, which then focuses the solar radiation. This method is employed when conveying solar radiation into a concentrator is more practical than using a single large collector.
Construction of Solar Furnace
The construction of a solar furnace typically involves the following components and steps:

- Selection of Location: Choose a suitable location for the solar furnace that receives ample sunlight throughout the year. Consider factors such as latitude, shading from surrounding structures or trees, and accessibility.
- Foundation: Prepare a solid foundation for the solar furnace structure, ensuring it is capable of supporting the weight of the mirrors, collectors, and receivers.
- Heliostats: Install a series of heliostats on terraces or a sloping surface. These heliostats are turnable mirrors that reflect sunlight in the same direction. Position them strategically to maximize sunlight collection and minimize shading between mirrors.
- Collector Structure: Build a large paraboloid or spherical reflecting collector structure using fixed mirrors. The collector should be designed to capture and focus sunlight onto a single point.
- Receiver: Install a small-volume receiver at the focal point of the collector. The receiver is the area where concentrated sunlight is absorbed and utilized for various applications.
- Mirror Preparation: Prepare the mirrors for the heliostats and collector. This involves grinding and polishing glass plates until they become optically flat. Then, coat them with aluminum or silver using vacuum evaporation and apply a suitable film for enhanced reflectivity.
- Mirror Mounting: Attach the prepared mirrors onto the heliostats and collector structure. Ensure secure and precise mounting to maintain accurate reflection angles.
- Tracking Mechanism: Implement a tracking system that allows the heliostats to follow the sun’s movement throughout the day. This can be achieved using hydraulic or electric driving mechanisms coupled with servo systems or time systems.
- Safety Measures: Incorporate appropriate safety measures, such as fencing or barriers, to prevent accidental exposure to concentrated sunlight and protect personnel working near the solar furnace.
- Integration and Testing: Connect the heliostats, collector, receiver, and tracking system to ensure proper functioning. Perform thorough testing and adjustments to optimize the solar furnace’s performance.
It’s important to note that the construction of a solar furnace can vary depending on its intended application, scale, and specific design considerations. Consulting with experts in solar thermal systems and following relevant safety guidelines are crucial during the construction process.
Applications of Solar Furnace
A solar furnace used for studying ceramics at high temperatures is a specialized device that allows scientists to investigate the properties of ceramics under extreme heat conditions. It offers a way to measure various physical properties such as melting points, changes in phases, specific heat, thermal expansion, thermal conductance, magnetic susceptibility, and thermionic emission.
The solar furnace achieves these high temperatures by using concentrated sunlight instead of conventional laboratory methods like flames or electric currents. It enables researchers to reach temperatures beyond what can typically be achieved in a lab setting.
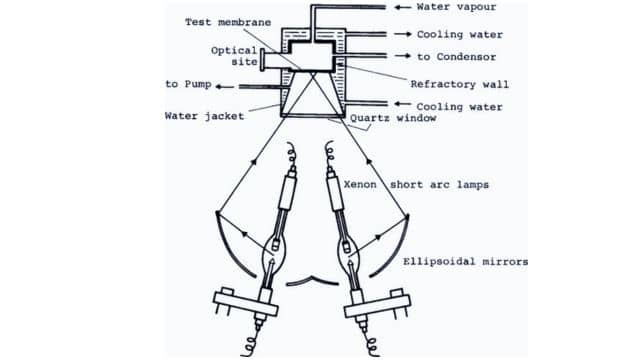
Scientists can perform important metallurgical and chemical processes at these high temperatures within the solar furnace. This includes tasks such as purifying materials or causing substances to sublime (transition directly from solid to gas) at elevated temperatures.
In simple terms, a solar furnace for studying ceramics at high temperatures is a powerful tool that allows scientists to heat ceramics to extreme levels using sunlight. This helps them understand how ceramics behave and change under such intense conditions, leading to advancements in various fields such as materials science, metallurgy, and chemistry.
Advantages of Solar Furnace
- It gives an extremely high temperature.
- Contamination by ions does not occur in fusion which might happen in the case of plasma or oxy-hydrogen flame
- A proper desirable atmosphere can be provided to the specimen.
- In a solar furnace, heating is carried out without any contamination, and temperature is easily controlled by changing the position of the material in focus.
- It provides very rapid heating and cooling. 4. Various property measurements are possible on an open specimen.
Disadvantages of Solar Furnace
- Solar furnaces have limitations as they can only be used on sunny days and for a limited duration of around 4-5 hours.
- Additionally, they can be expensive due to their complex design and specialized components.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a Solar furnace?
A solar furnace is indeed an instrument used to generate extremely high temperatures by concentrating solar radiation onto a specimen. It utilizes mirrors or lenses to focus sunlight onto a small area, creating intense heat that can reach temperatures of several thousand degrees Celsius.
What are the applications of Solar furnaces?
1. Environmental Remediation: Solar furnaces can be used in environmental remediation efforts, particularly for the treatment of hazardous waste and contaminated soil.
2. Solar-Powered Manufacturing Processes: Solar furnaces can be integrated into manufacturing processes that require high temperatures, such as metalworking, glass manufacturing, or ceramic production.What is the importance of solar furnaces?
The importance of solar furnaces lies in advancing scientific research, developing renewable energy, and reducing environmental impacts.
Read Also:
- Characteristics and Advantages of A.C. Over D.C. and Vice Versa
- Globalisation | Impacts of Globalisation
- Difference Between Filament Lamps and Fluorescent Tubes
- DIAC | Construction | Working and V-I Characteristics
- Electric Traction | Speed-Time Curve
- Dual Converter | Introduction, Operation Mode and Application




Leave a Reply