Table of Contents
UPS
UPS stands for Uninterruptible Power Supply as the name suggests is an arrangement to get continuous A.C. power for critical loads like computers, hospitals, and other emergency loads even in case of A.C. power/mains failure.
The main objective of a UPS system is to provide uninterruptible power to the critical load connected to it. The second main objective of a UPS is to provide clean and stable energy to sophisticated and sensitive electronic equipment. Critical loads like computer systems, communication systems, and continuous process industries require constant voltage supply. Moreover, failure of mains supply can cause loss of data in computers, wastage of materials in continuous process industries, etc. For that reason, these critical loads are continuously fed from UPS.
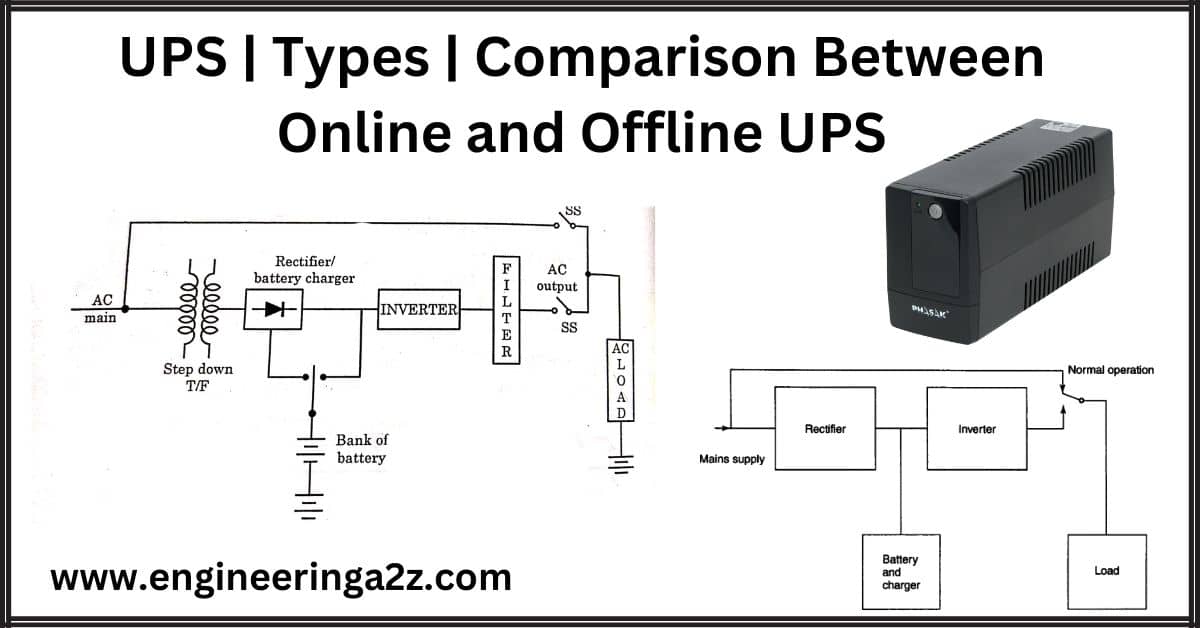
A U.P.S. is just such as alternative source. A static UPS generally consists of a rectifier, a battery charging unit, a battery bank, and an inverter. The rectifier converts the commercial AC input into de suitable input for the battery bank and the inverter. The system should be capable of supplying power to the inverter when the commercial supply is either slightly below the normal voltage or slightly above. The block diagram of a commonly used U.P.S. is shown in Figure.
Its basic parts are as follows:
(i) Battery charger: It is used for charging the battery. It transforms ac into dc. In order to prevent overcharging of the battery, it features specific V/I characteristics. It uses an SCR converter with a V/I controller to charge a drained battery steadily.
(ii) Bank of Battery: In the event that the main supply fails, it provides the full load current. Therefore, the option is determined by the load’s current, voltage, and duration, let’s say ten minutes.
(iii) Rectifier / Inverter: In order to get the desired constant supply frequency and voltage, the main supply is rectified to DC and then inverted. The inverter’s output should be sinusoidal.
(iv) Filter: It eliminates the higher-order harmonics.
(v) Switch: A static contactor switch is used to connect the load from the inverter or from the supply. It should be able to transition seamlessly to the other component after disconnecting the malfunctioning one. 10ms are needed for it to operate.
Types of UPS
There are mainly three types of UPS:
(i) Offline UPS
(ii) ON line UPS
(iii) Line-interactive UPS.
These types are explained in this chapter one by one.
1. Off-Line UPS
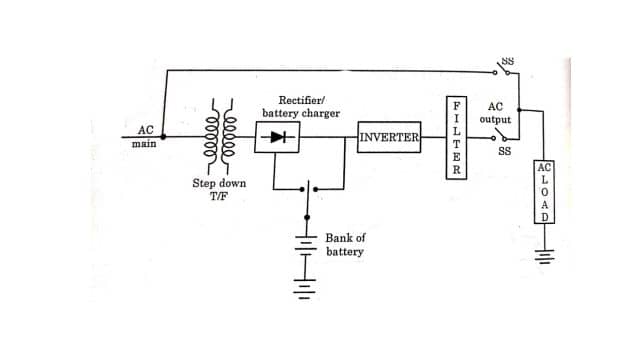
In the offline, UPS filters the mains and feeds it directly to the load for most of the time. In the offline UPS, the inverter is normally in the off state. When the main supply is not available, load is automatically switched by the static contractor switch, to an inverter. The offline UPS is also known as the stand-by mode of UPS because the inverter is on stand-by as long as the commercial/main power source is not available. When the supply is restored, the inverter is again shut off.
The block diagram of offline UPS is shown in Figure. An offline UPS switches on the battery power via a DC to AC inverter when it detects a power loss or drop. And this process takes a certain small but finite time. It is typically four milliseconds. That is why offline UPS is also known as short-break UPS. This system is cheaper than the online system.
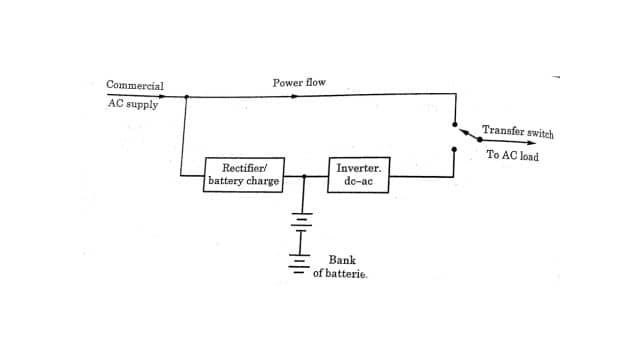
2. On-Line UPS
In this system, the load is always fed by the inverter. Therefore, the rectifier and inverter are always on. The figure gives the block diagram of an online UPS. It consists of a rectifier unit/battery charger that converts AC to DC and charges the battery. The block of system logic and control unit senses the ac mains continuously and is linked with a charger, inverter, and transfer switch. If the inverter becomes faulty the load is fed directly from the main supply.
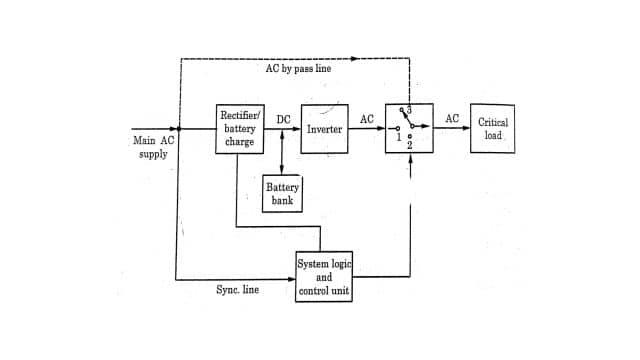
Online UPS has three modes of operation:
- When input supply is available: In this case the main supply directly feeds the load through the rectifier and inverter circuit. This battery is in charged condition. It is known as the normal mode.
- When input supply is not available: In this case, the battery feeds the load through the inverter. It is known as outage mode.
- Bypass mode: When the fault develops in UPS or inverter, then this mode will exist. In this mode, the bye-pass switch automatically transfers the load to the main supply line.
Online UPS systems offer the best protection, but they are the most expensive, biggest, and heaviest as well.
3. Line Interactive UPS
The line-interactive UPS system came out due to the off-line UPS’s inability to provide an acceptable output voltage to the connected equipment during brown-out conditions. Interestingly, however, many stand-by models now have a voltage regulation feature. A “brow. out” happens when the utility voltage remains excessively low for a sustained period. Under these conditions, the offline UPS would go to battery operation and if the brownout was sustained long enough, the offline UPS battery would become fully discharged and not be able to be turned back on until the utility voltage returned to normal. To prevent this from happening a voltage regulating transformer was added.
Hence the term line interactive UPS was born. This feature really does help as low voltage utility conditions are common. Again when selecting a line-integrative UPS, it is always best to select a model with a true sine wave output. Several manufacturers have models available that will accept extended battery packs to provide additional battery runtime. This type of UPS typically costs more than the offline type but is worth the additional cost.
Comparison between Online UPS and Offline UPS
| Sr. No. | ON-Line UPS | OFF-Line UPS |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | It supplies the power continuously to the load i.e. 24 hours a day. This means the inverter is ON all the time. | It is the least expensive type. |
| 2. | The running time of the inverter is generally 10 min to 30 min. | Most expensive, biggest, and heaviest in size. |
| 3. | It is the least expensive types. | Its running time is generally 10 min to 30 min also. |
| 4. | Its switching time is generally 0 ms. | It is the least expensive type. |
| 5. | It is used for network environments e.g. file servers supporting many users. | It is sufficient for a stand-alone PC. |
| 6. | It gives sine-wave output. | It gives a square wave or sine wave output. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is an uninterrupted power supply (UPS)?
The system which provides an interruption-free supply of a.c is called UPS. It can be offline or on-time UPS.
What is redundancy UPS?
The system of transferring the critical load from a failed UPS to an attenuated power source (or other standby UPS) without interruption of ac to the critical load.
What is a switched-mode power supply (SMPS)?
In low to medium power requirements, a dc power supply is required – Switched-mode power supply is a multistage de-supply and is used for higher ratings.
Read Also:
- Difference Between A.C. and D.C.
- FACTS Controller | Types of FACTS Controller
- Advantages | Disadvantages and Applications of Electric Power
- Dual Converter | Introduction, Operation Mode, and Application
- Stand Alone PV System | Schematics and its Components




Leave a Reply