Table of Contents
Introduction
Production management is the practice of overseeing and controlling a company’s operations to efficiently create the goods and services it intends to produce. This involves planning, coordinating, and managing the various steps involved in turning raw materials into final products.
A key part of production management is implementing the company’s production strategy, which includes choosing specific technologies and achieving predetermined goals related to factors like production costs, product quality, and manufacturing capabilities.
In practical terms, production management involves overseeing and directing individuals or teams responsible for tasks such as manufacturing, equipment maintenance, quality assurance, and inventory control. Essentially, it’s about acquiring and efficiently using resources like management expertise, raw materials, labor, funds, machinery, and more to bring about the production of finished goods. In a nutshell, production management is the process that bridges the gap between planning and producing the final products.
Objectives of Production Management
The objectives of production management include:
- Efficient Resource Utilization:
- Efficiently allocating and utilizing labor, materials, and machinery is essential for minimizing waste and maximizing productivity. It involves optimizing workforce schedules, managing inventory effectively, and ensuring machinery is utilized to its fullest capacity.
- High-Quality Products:
- Meeting customer demand with high-quality products is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction and brand reputation. Quality control measures and rigorous testing processes should be in place to ensure product consistency and reliability.
- Cost Reduction:
- Reducing production costs is a continuous effort to increase profitability. This can involve streamlining processes, negotiating favorable material prices, minimizing waste, and implementing energy-efficient practices to lower operational expenses.
- On-Time Delivery:
- Meeting delivery deadlines is vital to fulfill customer orders and maintain customer trust. Effective production scheduling, inventory management, and logistics coordination are necessary to ensure on-time delivery.
- Productivity and Capacity Optimization:
- Optimizing productivity and capacity involves maximizing output while minimizing resource consumption. This can be achieved through process automation, lean manufacturing techniques, and regular equipment maintenance to avoid downtime.
- Continuous Process Improvement:
- Implementing a culture of continuous improvement encourages employees to identify and eliminate inefficiencies. Techniques such as Six Sigma, Lean, and Kaizen can be used to systematically improve processes and boost overall efficiency.
- Effective Departmental Coordination:
- Effective coordination among different departments (e.g., production, logistics, quality control, and sales) is crucial to ensure smooth operations. Collaboration, communication, and information sharing between departments help prevent bottlenecks and delays in the production process.
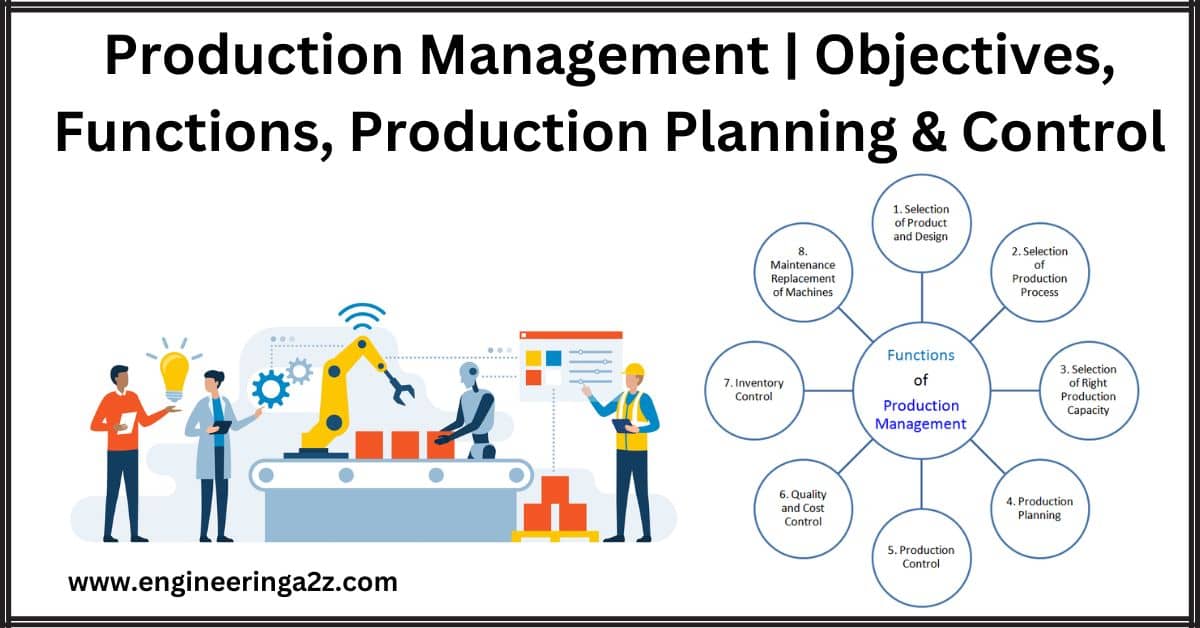
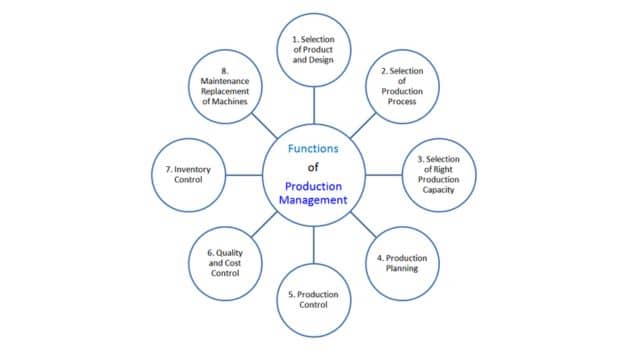
Functions of Production Management
Let’s simplify the components or functions of production management:
- Selection of Product and Design,
- Selection of Production Process,
- Selecting Right Production Capacity,
- Production Planning, Production Control,
- Quality and Cost Control, Inventory Control, and
- Maintenance and Replacement of Machines
The above functions of production management are briefly discussed below.
- Selection of Product and Design: Production management begins by choosing the best product to make. This choice is super important because it can make or break the company. They have to carefully evaluate different product options before deciding. Once they pick the product, they need to choose the right design for it. This design should match what customers want and give them the most value for their money. To make sure of this, production management uses methods like value engineering and value analysis to make the product as good as possible without costing too much.
- Selection of Production Process:
Production management is responsible for choosing the best way to make products. This includes picking the right technology, machines, and how materials are handled. It’s crucial for efficient and effective manufacturing. - Selecting Right Production Capacity: Production management has to figure out how much they can make to meet customer demand. If they make too little or too much, it causes issues. The manager plans the right amount of production for both short and long-term needs. They use break-even analysis to help with this planning.
- Production Planning: Production planning involves routing and scheduling. Routing determines the best sequence for operations, ensuring efficiency. Scheduling sets start and end times for each task, keeping production on track. Together, they ensure smooth and efficient manufacturing processes.
- Production Control: Production management involves production control. The manager watches over production, checking if it matches plans. If there are differences, they make corrections to keep things on track and meet the goals.
- Quality and Cost Control: Production management cares about quality and cost control because customers want good products at low prices. To meet this demand, managers work on improving quality and reducing costs.
- Inventory Control: In inventory production management, keeping an eye on inventory is crucial. We shouldn’t have too much or too little stuff in storage. Too much ties up money and can lead to waste, while too little can cause problems with production.
- Maintenance and Replacement of Machines: Production management takes care of machines and equipment. Managers set up a system for regular checks, cleaning, and fixing machines to prevent breakdowns and keep production running smoothly.
Production Planning and Control
Production planning and control (PPC) is an integral part of production management. It involves the following key aspects:
- Planning: This phase involves setting production objectives, determining the required resources (such as labor, materials, and equipment), and creating a production schedule that aligns with customer demand and overall business goals.
- Routing: Routing defines the sequence of operations and processes that a product or service must go through during production. It specifies the flow of materials and the order in which tasks are to be performed.
- Scheduling: Scheduling involves assigning specific start and end times for each production task based on the production plan. It ensures efficient utilization of resources and adherence to the production timeline.
- Dispatching: Dispatching is the act of releasing production orders to the shop floor or relevant departments. It communicates the details of each job, including what needs to be produced, when, and where.
- Follow-up and Control: This phase involves monitoring the progress of production orders, tracking actual performance against the plan, and making adjustments as needed to ensure that production goals are met. It also involves quality control and addressing any issues that may arise during production.
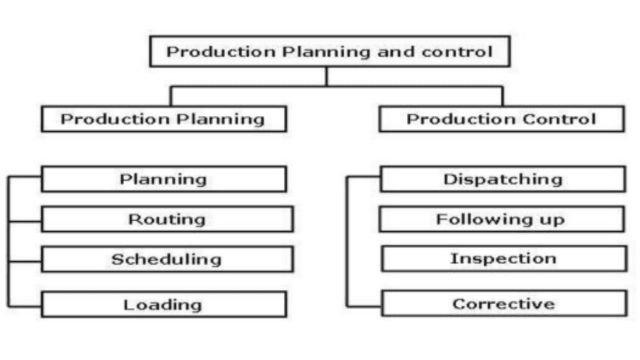
In summary, production planning and control is a vital component of production management that focuses on the systematic planning, execution, and monitoring of production activities to achieve efficient and effective production outcomes. It plays a crucial role in optimizing resource allocation, minimizing lead times, and ensuring customer satisfaction.
Characteristics of Production Management
- Production Management involves efficient planning and control. It oversees the activities of the part of a company responsible for turning raw materials into final products.
- It is closely tied to the production process, ensuring that goods and services are created in line with specific quantity requirements and demand patterns while minimizing expenses.
- Production Management consists of a collection of fundamental principles that guide production activities. These principles encompass various aspects such as cost-saving measures, facility layout, job organization, scheduling, quality assurance, inventory management, work analysis, and financial control.
Example of Production Management
Black Current, a small company specializing in manufacturing optimal wires for electric appliances, recently hired a new production manager under the guidance of the general manager. The production department falls under the umbrella of four key departments: process, quality, maintenance, and planning.
In the job description provided by the general manager, specific objectives were outlined for the production manager to achieve within the first year of their tenure. These objectives include:
- Reducing Production Costs: The production manager’s primary goal is to achieve a 5% reduction in production costs. This will require the efficient allocation of labor, materials, and technology resources.
- Maintaining High Quality Standards: It is crucial for the production manager to ensure that the company maintains high-quality standards in the manufacturing process.
- Managing Inventory Levels: The production manager is responsible for maintaining inventory levels equivalent to approximately three weeks of sales. This ensures a smooth supply chain and customer satisfaction.
- Increasing Manufacturing Capacity: A significant task assigned to the production manager is to plan and execute a project that will increase the company’s manufacturing capacity by 56%. This expansion is essential to meet growing demand.
To achieve these objectives, the new production manager plans to implement specific strategies like lean manufacturing. These strategies aim to streamline operations, reduce waste, and improve overall efficiency in production processes. With these tactics in place, the production manager is confident in their ability to successfully meet the outlined goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the main purpose of production management?
The primary aim of production management is to efficiently plan, organize, and control manufacturing processes to produce goods and services that meet quality standards, fulfill customer demand, minimize costs, and maximize overall productivity and profitability.
What are the 5 of production management?
The five key elements of production management encompass planning, organizing, directing, coordinating, and controlling manufacturing operations to optimize resource allocation, enhance product quality, meet production goals, and streamline processes within an organization.
What are the 4 main types of production?
The four main types of production are:
1. Job Production: Customized, one-of-a-kind products made to order.
2. Batch Production: Producing a limited quantity of similar items at once.
3. Mass Production: Large-scale manufacturing of standardized products.
4. Continuous Production: Non-stop production of identical goods with minimal interruption.What are the two major types of production?
The two major types of production are:
1. Goods Production: This involves manufacturing physical products or goods, such as electronics, automobiles, or clothing.
2. Service Production: This pertains to providing intangible services to customers, like healthcare, education, banking, or consulting.
Read Also:
- Energy Management | Need and Environmental Aspects
- Marketing Management | Objectives & Functions of Marketing Management
- Management | Process & Functions of Management
- Markets: Perfect competition, Monopoly, Monopolistic & Oligopoly
- Overvoltage Protection | Internal and External Causes Of Overvoltage




Leave a Reply