Table of Contents
Introduction
Two-port networks simplify complex electrical circuits. They represent components like transmission lines and transformers, as well as electronic ones like transistors. This overview explains two-port network parameters, how to calculate them, and conditions for symmetry and reciprocity, aiding in network analysis.
What is a Two-Port Network?
A port is a pair of terminals where current enters one and exits the other. Components like resistors, inductors, and capacitors are examples of one-port networks, where electrical interactions occur at a single pair of terminals.
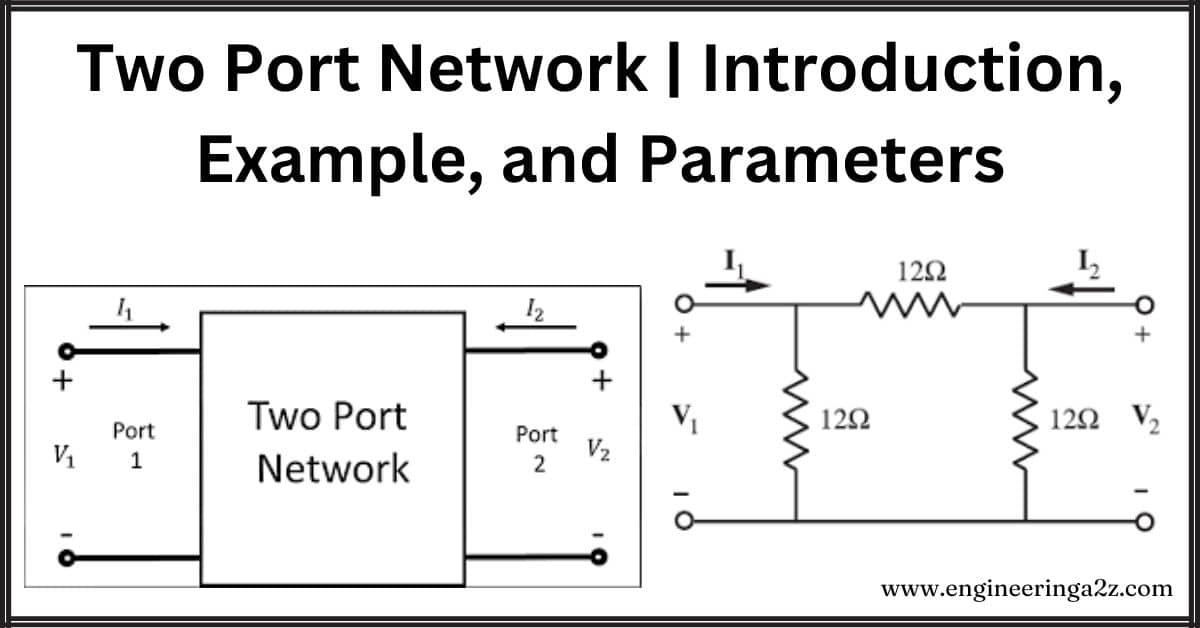
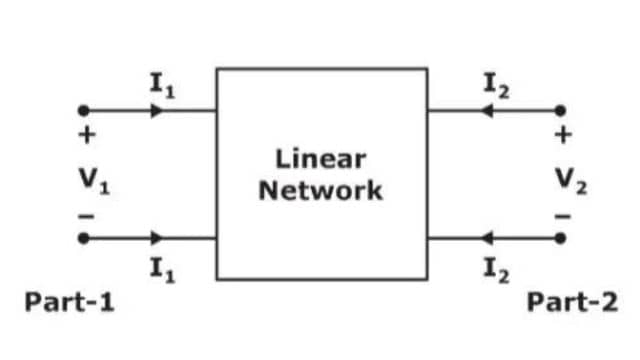
A two-port network has two pairs of terminals, here named port 1 and port 2. V1 and V2 represent the voltages at these ports, while I1 and I2 represent the currents flowing through the respective ports.
Two Port Network Example
A few examples of Two Port Network are:
- Filters,
- Small-signal models for transistors
- Matching networks,
- Transmission lines,
- Transformers,
Two Port Network Parameters
In a two-port network, you can provide input to any port and extract output from any port. The parameters used to describe such networks are called two-port network parameters. There are six sets of these parameters, named Z, Y, T, T’, h, and g parameters, involving voltage (V) and current (I).
Z Parameters
In a two-port network, with I1 and I2 as inputs and V1 and V2 as outputs, the Z parameters describe the relationship:
- V1 = Z11 * I1 + Z12 * I2
- V2 = Z21 * I1 + Z22 * I2
Z11 is found by making port 2 an open circuit when I2 is 0, and Z12 is found by making port 1 an open circuit when I1 is 0. Similarly, Z21 and Z22 are obtained. These parameters are called impedance parameters or Z parameters. They represent the ratio of output voltage to input current and are measured in Ohms (Ω).
- A two-port network is symmetrical if Z11 equals Z22.
- A two-port network is reciprocal if Z12 equals Z21.
Y Parameters
In a two-port network, considering V1 and V2 as inputs and I1 and I2 as outputs, the Y parameters describe the relationship:
- I1 = Y11 * V1 + Y12 * V2
- I2 = Y21 * V1 + Y22 * V2
Y11 is found by making port 2 a short circuit when V2 is 0, and Y12 is found by making port 1 a short circuit when V1 is 0. Similarly, Y21 and Y22 are obtained. These parameters are called admittance parameters or Y parameters, representing the ratio of output current to input voltage, measured in mhos (℧).
- A two-port network is symmetrical if Y11 equals Y22.
- A two-port network is reciprocal if Y12 equals Y21.
T Parameters
In a two-port network, with V2 and I2 as inputs and V1 and I1 as outputs, the T parameters (Transmission parameters) describe the relationship:
- V1 = AV2 – BI2
- I1 = CV2 – DI2
Here, A, B, C, and D are constants obtained under specific conditions:
- A = V1/V2 when I2 is 0
- B = -V1/I2 when V2 is 0
- C = I1/V2 when I2 is 0
- D = -I1/I2 when V2 is 0
A and D have no units, while B and D have units of ohms (Ω) and mhos (℧), respectively. The ABCD parameters are also known as T parameters. A and C are obtained by making port 2 an open circuit, while B and D are obtained by making port 2 a short circuit.
- A two-port network is symmetrical if A equals D.
- A two-port network is reciprocal if AD – BC equals 1.
T’ Parameters
In a two-port network, with V1 and I1 as inputs and V2 and I2 as outputs, the T’ parameters (Inverse Transmission parameters) describe the relationship:
- V2 = A’V1 – B’I1
- I2 = C’V1 – D’I1
Here, A’, B’, C’, and D’ are constants obtained under specific conditions:
- A’ = V2/V1 when I1 is 0
- B’ = -V2/I1 when V1 is 0
- C’ = I2/V1 when I1 is 0
- D’ = -I2/I1 when V1 is 0
A’ and D’ have no units, while B’ and D’ have units of ohms (Ω) and mhos (℧), respectively. The A’B’C’D’ parameters are also known as Inverse Transmission parameters or T’ parameters. A’ and C’ are obtained by making port 1 an open circuit, while B’ and D’ are obtained by making port 1 a short circuit.
- A two-port network is symmetrical if A’ equals D’.
- A two-port network is reciprocal if A’D’ – B’C’ equals 1.
h Parameters
In a two-port network with I1 and V2 as inputs and V1 and I2 as outputs, the h parameters (Hybrid parameters) describe the relationship:
- V1 = h11 + h12V2
- I2 = h21I1 + h22V2
Here, h12 and h21 are unitless, and the units of h11 and h22 are ohms (Ω) and mhos (℧), respectively. The h parameters can be obtained under specific conditions:
- h11 = V1/I1 when V2 is 0
- h12 = V1/V2 when I1 is 0
- h21 = I2/I1 when V2 is 0
- h22 = I2/V2 when I1 is 0
Two h parameters, h11, and h21, can be found by making port 2 a short circuit, and the other two, h12 and h22, can be found by making port 1 an open circuit.
- A two-port network is symmetrical if h = 1, i.e., h11h22 – h21h12 = 1.
- A two-port network is reciprocal if h12 equals -h21.
g Parameters
In a two-port network with V1 and I2 as inputs and I1 and V2 as outputs, the g parameters (Inverse Hybrid parameters) describe the relationship:
- I1 = g11V1 + g12I2
- V2 = g21V1 + g22I2
Here, g12 and g21 are unitless, and the units of g11 and g22 are mhos (℧) and ohms (Ω), respectively. The g parameters can be obtained under specific conditions:
- g11 = I1/V1 when I2 is 0
- g12 = I1/I2 when V1 is 0
- g21 = V2/V1 when I2 is 0
- g22 = V2/I2 when V1 is 0
Two g parameters, g11, and g21, can be found by making port 2 an open circuit, and the other two, g12 and g22
Two g parameters, g11, and g21, can be found by making port 2 an open circuit, and the other two, g12 and g, can be found by making port 1 a short circuit.
, can be found by making port 1 a short circuit.
- A two-port network is symmetrical if g = 1, i.e., g11g22 – g12g21 = 1.
- A two-port network is reciprocal if g12 equals -g21.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is meant by the two-port network?
A two-port network is an electrical network or circuit with two pairs of terminals, allowing independent input and output variables. It’s commonly used to model complex systems in a simplified manner.
What is the use of two-port?
A two-port is used to model and analyze complex electrical systems, simplifying their representation. It aids in understanding and designing circuits, facilitating the study of signal flow and interactions.
What is the formula for 2 ports?
The general representation of a two-port network involves four variables: V1 and I1 as input voltage and current, and V2 and I2 as output voltage and current. Different parameter sets like Z, Y, T, h, and g parameters express the relationships between these variables.
How many numbers is a port?
A port in a two-port network consists of a pair of terminals through which electrical signals enter and exit. A two-port network has two such ports, providing input and output connections.
Read Also:
- Maximum Power Transfer Theorem | Formula, Proof, and, Limitations
- Superposition Theorem | Procedure, Limitations, and Applications
- Norton’s Theorem
- Reciprocity Theorem | Statement, Limitations, and Applications




Leave a Reply