Table of Contents
Gas Turbine Power Plant
The generating gas turbine power plant in which gas turbine are used as prime mover for generation of electrical energy are called Gas Power Plant. In gas turbine power plant we uses the Brayton cycle. Gas turbine burns fuel such as oil, natural gas and powered coal. Instead of using the heat to produce steam as in steam turbine gas turbine use the hot gases to start the turbine blades.
Working of Gas Turbine Power Plant
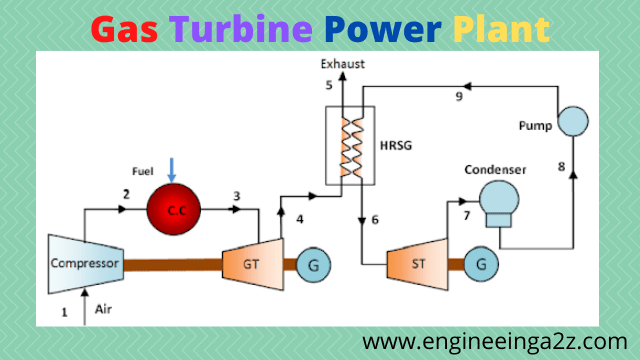
In gas turbine power plant air is used as working fluid. The air is compressed by means of a compressor and is fed to the combustion chamber where heat is also added in the chamber thus raising the temperature of the air. From this combustion chamber, the hot and high pressure air is passed to the prime mover i.e. gas turbines where it expands and does the mechanical work. These gas turbines which are coupled to the alternators, drive the alternator which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
It may be noted here that compressor gas turbine and alternator are mounted on the same shaft so that a part of mechanical energy can be utilised for the operation of compressors. These plants are used as standby plants for hydro-electric stations as a starting plant for driving the different auxiliaries in power plant etc .
Diagram of Gas Turbine Power Plant
Components of Gas Turbine Power Plant
1. Gas Turbine
A gas turbine is also known as combustion turbine. It is a type of internal combustion engine. It has an upstream rotating compressor coupled to a downstream turbine and a combustion chamber in the middle section.
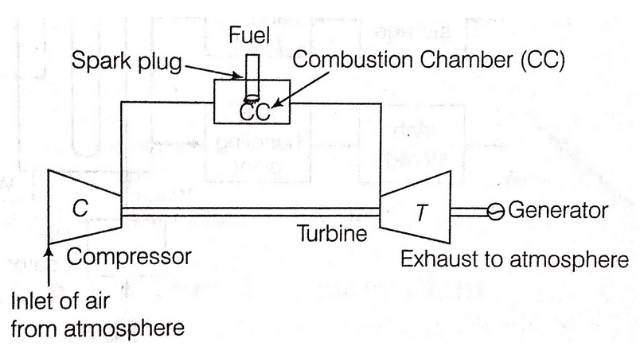
The basic operation of gas turbine is similar to that of the steam power plant (discussed ahead) except that air is used instead of water fresh atmospheric air flows through a compressor that brings it to higher pressure. Energy is then added by spraying fuel into the air and igniting it so that combustion generate a high temperature flow.
This high temperature and high pressure gas enter a turbine, where it expands down to the exhaust pressure, producing a shaft work output in the process. The turbine shaft work is used to drive the generator and compressor, which are coupled to the shaft.
The energy that is not used for shaft work comes out in the exhaust gases. Gas turbines are used to power aircraft, trains, ships and electrical generators etc.
2. Compressor
The compressor used in gas turbine power plant is generally of type The air is drawn by the compressor from the atmosphere via the filter. The filter removes the dust from air. The rotary blades of the compressor push the air between stationary blades and raise the pressure. Thus air at high pressure is available at the output of the compressor.
3. Combustion Chamber
It consists of a vessel into which the air at high pressure from the compressor is fed: In the combustion chamber, heat is added to the air by burning oil. The oil is injected to the combustion chamber through the burner at high pressure to ensure atomisation of oil and us thorough mixing with air. The result of this combustion chamber attains a very high temperature of around 3000°F. The combustion gases are suitably cooled to 1400°F and then delivered to the gas turbine.
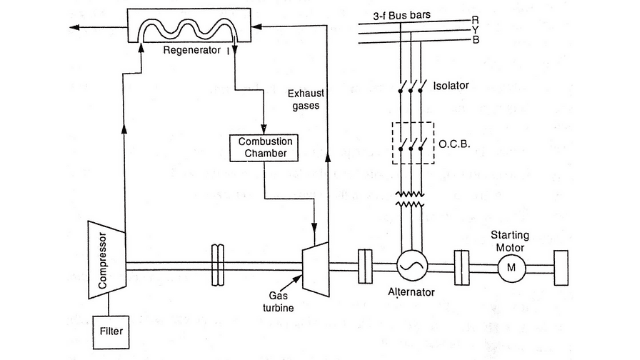
4. Regenerator
It is a device used in gas turbine power plant. The function of this is to recover heat from the exhaust gases of the turbine. The exhaust gases are made to pass through the regenerator before wasting to the atmosphere. A regenerator is a nest of tubes contained in a shell The compressed air from the compressor passes through the tubes on its way to combustion chamber. In this way, compressed air is heated by the hot exhaust gases.
5. Alternator
The alternator is coupled to the gas turbine. The alternator converts mechanical energy of the turbine into electrical energy. The output of the alternator is given to bus bars through the transformer, circuit breakers and isolators.
6. Starting motor
An electric motor is used to start the compressor before starting the turbine, the electric motor and turbine are mounted on the same shaft. The motor is energised by the batteries Once the unit starts, a part of mechanical power of the turbine drives the compressor and there is no need of motor now.
Salient Features of the Gas Turbine Power Plant
The overall efficiency of gas turbine plant also called the open cycle plants is very low. As a major part (about 65%) of the power developed is utilised in driving the compressor. The hot gases from the combustion chamber are cooled down to a low safe temperature before admitting it to the turbine. This also reduces the efficiency. Therefore, the overall efficiency does not exceed 20%
Advantages of the Gas Turbine Power Plant
- The construction of this power plant is quite simple as compare to steam power plant because there is no need of boiler and their auxiliaries.
- The gas turbine power plant requires low initial cost.
- The gas turbine power plant are more reliable.
- The building space required for gas turbine power plant should be small.
- The gas turbine power plants can be started quickly and can be put to share full load within few minutes.
- The maintenance cost of such plants is very low as compared to diesel power plants.
- There are no standby losses. In a steam power station, these losses occur because boiler is kept in operation even when the steam turbine is supplying no load.
Disadvantages of the Gas Turbine Power Plant
- The gas turbine unit has got starting problems because the compressor has to be started. before the starting of the turbine. The compressor requires power supply for starting from some external source However, once the unit starts, the external power is not needed, as the turbine itself supplies the necessary power to the compressor.
- The net output of the unit is low as a greater part of power developed by the turbine is used in driving the compressor.
- The temperature of combustion chamber is quite high about 3000 F and therefore its life is comparatively reduced
- The overall efficiency of such plants is very low, about 20% because the exhaust gases from the turbine contain sufficient heat.
- The gas turbine power plants have noisy operation, high specific fuel consumption and limited unit capacity.
Selection of site for Gas Turbine Power Plant.
- The site should be as near to the load centre as possible so that the cost of transmission of power and losses should be minimum.
- The site should be far away from the thickly populated area because of its noisy operation.
- The land required for gas turbine power plants should be of cheap rate in order to keep the capital cost of the plant low.
- The bearing capacity of the land should be high to withstand the load of the plant and vibrations transmitted to the foundation from compressors and turbines.
- The fuel required for the plant should be easily available and at reasonable rates.
- The transportation facilities should be available.
Read More :
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Which gas is used in gas power plant?
Natural gases are used in gas power plant such as methane or any flammable gas or light distillate petroleum products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel and kerosene (paraffin) which happen to be available locally, though natural gas is the most commonly used fuel.
Why the gas power plant has lower efficiency?
The overall efficiency of gas turbine plant also called the open cycle plants is very low. As a major part (about 65%) of the power developed is utilised in driving the compressor. The hot gases from the combustion chamber are cooled down to a low safe temperature before admitting it to the turbine. This also reduces the efficiency. Therefore, the overall efficiency does not exceed 20%
What are the application of gas turbine power plant?
The gas turbine plants are used for the following
1. Power Generation
2. Oil and gas industries
3. Used to dry the generator
4. Petrochemical industries
5. Power Generation




Comments (4)
Great content 😊😍
I am really impressed along with your writing skills and also with the layout
for your weblog. Is that this a paid theme or did
you modify it yourself? Either way stay up the nice high
quality writing, it is uncommon to peer a nice weblog like this one these days..
It is very helpful about power Generation and also gather knowledge how to generate electricity.
Thank you for your comment 😊
Stay connected with us to increase your knowledge and read more content.