Table of Contents
First Generation Operating System
- The initial generation of machines was also referred to as vacuum tubes.
- Each machine was designed, constructed, programmed, operated and maintained by a single group of workers.
- Thousands of wires were used to link the plugboard electrical circit for programing.
- The programmer would utilize the sign-up sheet on the wall to reserve a specific time.
- After that, they would head to the machine room, plug their plugboard into the computer and wait for a few hours, praying that none of the around 20000 vacuum tubes would burn out while the machine ran
| Year | 1940-1950 |
|---|---|
| Programming language | Machine language |
| Operating system | Unheard |
| Hardware | Vacuum tubes, plugboard, Cables |
| Computers | ENIAC, Z3, Colossus |
Second Generation Operating System
- Second Generation OS : Transistors and Batch Systems were other names for second-generation computers.
- In this generation, computers were dependable devices made to be sold to clients such as government organization and academic institutions.
- Different teams were established to focus on the planning, constructing and programming of computer system.
- Mainframes, as they were called, were maintained in different rooms and contained computers.
- Different machines were constructed for input/output and calculating.
- Programs were referred to as jobs. Jobs were entered into batches or groups.
- Physics and engineering computations were performed using second generation computers in science and engineering..
| Year | 1950 -1960 |
|---|---|
| Programming language | IBM’s operating system FM |
| Operating system | IBM’s operatinf system FM |
| Hardware | Transistors and Batch Systems, punch card, magnetic tape |
| Computers | Mainframe, IBM 1401, IBM 7094 |
Third Generation Operating System
- Third-generation computers had multiprogramming and integrated circuits (ICs)
- Because it was difficult to maintain two computers, IBM released its first computer names.
- System 360 is an integrated circuit based system.
- This generation primary goal was to make all software, including the OS/360 operating system, compatible with all models.
- One significant innovation in this generation was multiprogramming, which allowed for the CPU to be used by another project while the first one waited for I/O to finish.
- In this manner, the CPU’s maximum utilization might be attained.
- Spooling capable of reading tasks from cards onto the disk.
- Time sharing, where multiple user use the CPU in turns massive commercial data processing operations and extensive research calculations were conducted using third generation computers.
| Year | 1960-1970 |
|---|---|
| Programming language | Integrated Circuit |
| Operating system | Linux MINIX |
| Hardware | Integrated circuit |
| Computers | System/360. |
Fourth Generation Operating System
- Personal computers were another name for fourth generation computers.
- Microchips allowed for the creation of incredibly compact computers, enabling each person to have their own persnal computer.
- Businesses like IBM and Intel began developing operating systems for their individual CPUs
- Designed with ease of use in mind, the graphical user interface
- In this age, Microsoft introduced many Windows versions – network operating systems and distributed systems gained popularity with network operating systems, users may access distant workstation and transfer files between them.
- A distributed operating system, albeit consisting of several processors, presents itself to consumers as a solitary uniprocessor machine..
| Year | 1970–1990 |
|---|---|
| Programming language | High level programming language |
| Operating system | DOS, Windows, UNIX, FreeBSD |
| Hardware | LSI (large Scale Integration) circuit, chips, transistors |
| Computers | IBM 4341, DEC 10, STAR 100 |
Fifth Generation Operating System
- The fifth generation, which used Ultra Large Scale Integrated Chips, was also referred to as a mobile computer.
- The market saw the rise in popularity of new operating systems including as Symbian, Blackberry OS, iOS and Android. Additionally devices got more compact & portable.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) was heavily utilized in the creation of devices that analyzed input using natural language processing
| Year | 1990–Present |
|---|---|
| Programming language | High level programming language |
| Operating system | Handheld devices, wearable devices, PDAs, smartphones |
| Hardware | Ultra large scale integrated chip |
| Computers | Handheld devices, wearable devices, PDAs, Smartphone |
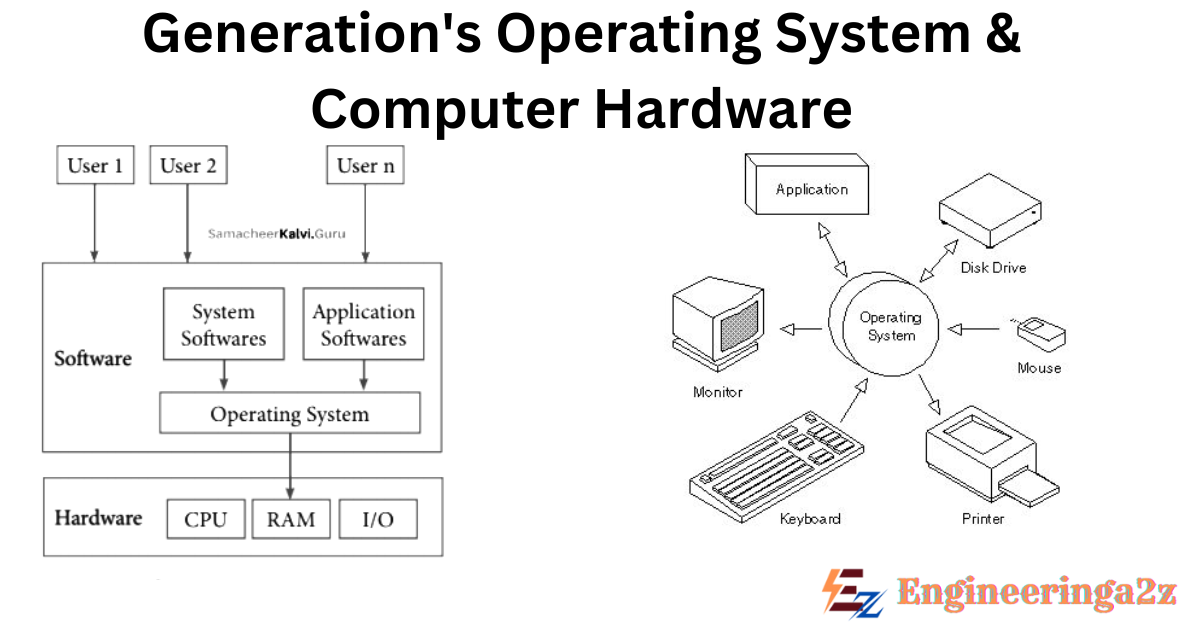
Computer Hardware
Processor
- The CPU is the most important part of any computer. It fetches instructions from memory, understands them and then does what the instructions say .
- CPUs have registers within to store temporary data & important variables.
- The program counter, a special register, holds the memory address of the subsequent instruction that needs to be retrieved.
- Condition code bits are contained in the Program Status Word..
- The introduction of Multithreading (also called hyperthreading) lets a CPU deal with more than one task at once. For example:- Intel Pentium 4’s CPU could handle two tasks and switch between them quickly
- A GPU is like a CPU but has many small cores. It’s great for doing many calculations at the same time, especially when making graphics for games & programs.
Memory
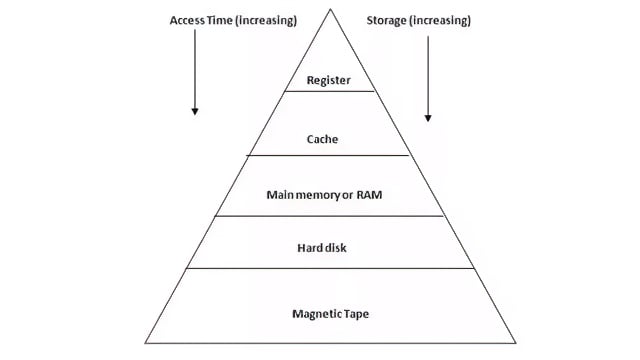
- The basic expectations from the memory is its speed, storage and performance but a single memory is not capable of fulfilling the same
- Memory system is based on hierarchy of layers.
- Registers inside the CPU forms the top layer in the hierarchy which gives quick access to data.
- Next is cache memory.. It stores data that the computer uses a lot, so it can be found quickly.
- There are two kinds of cache: L1 & L2. L1 cache is always inside the CPU and is very fast. L2 cache is bigger and stores more data,but it is a bit slower.
- The main difference between L1 and L2 cache is how quickly they give information to the CPU
Booting Process in Computer
- Booting means starting up a computer by loading its main software called the Kernel.
- The computers main board has program called BIOS. BIOS checks the memory (RAM) & important parts inside the computer when the machine is switched on.
- If everything looks fine, BIOS starts the process to load the computer hard drive or other boot device
- Computer reads the very first piece of information from this device & runs it.
- After that.. a second program called a bootloader is loaded from memory & gets things ready for the operating system to start .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is an operating system (OS)?
Operating system is a software that manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services for computer programs. Think of it as the manager of your computer.
-
How are operating systems classified by generation?
Operating systems are typically classified into generations based on their development and evolution. Common generations include batch processing systems (1st generation), multiprogramming systems (2nd generation), time-sharing systems (3rd generation)and modern graphical user interface systems (4th generation).
-
What is computer hardware generation?
Computer hardware generation refers to the different phases of development and technological advancements in computer components. Each generation is characterized by improvements in speed, size & capabilities of processors, memory, storage and other peripherals.
-
What is a GUI?
GUI (Graphical User Interface) is a user friendly interface that uses visual elements like windows, icons and menus for interaction, unlike command-line interfaces.
Related Posts
- BTech Computer Science Engineering Previous Years Question Papers PDF
- PLC and Microcontroller Notes PDF (Handwritten)
- Organizational Computational Models
- Processes and Threads in Operating System
- Internet of Things | Functional Block of IoT, Characteristics and Application
- OSI Model | Seven Layers Of OSI Model and Working













Leave a Reply