Table of Contents
Operating System
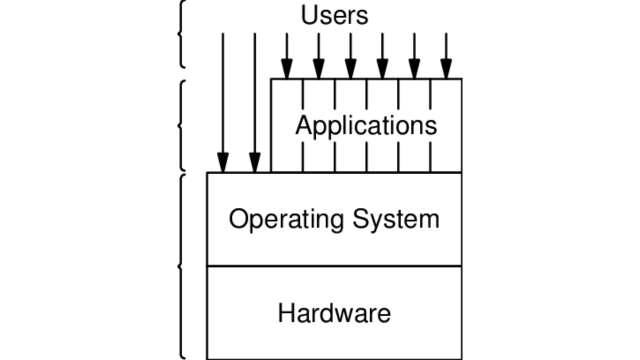
An operating system serves as a bridge or interface between a computer’s user and its hardware. An operating system’s job is to give users a convenient and effective environment in which to run programs.
- An operating system is a program that controls and run the execution of application programs and acts as a user interface between the user of a computer and the computer hardware.
- The distribution of resources and services, including memory, processors, devices and data, is the responsibility of an operating system. In order to manage these resources, the operating system comprises programs like a scheduler, memory management module, I/O programs, traffic controller and file system.
Functions of Operating System
The operating system performs three functions :
- Convenience for user : An OS makes a computer more convenient for programmers to use.
- Efficiency of memory : An operating system allows the computer system resources to be used efficiently with no interruption.
- Adaptability : An operating system should be designed to facilitate seamless development, testing and integration of new system functions without disrupting ongoing services. This is an important function of operating system.
Operating System as User Interface
- All general-purpose computers have the following components: operating system, application programs, system programs and hardware. Memory, CPU, ALU, I/O devices, peripherals and storage devices make up the hardware. Compilers, loaders, editors, operating systems etc.. are all part of the system program. A business program and a database program make up the application program.
- For other programs to run on a computer, an operating system is required. The operating system manages how different systems and application programs for different users use the hardware. It offers a setting where other programs can operate effectively.
- The operating system is a set of special programs that run on a computer system that allow it to work properly. Basic functions include sending output to the display screen, managing peripheral devices, tracking files and directories on the disc and recognizing input from the keyboard.
Input/Output System Management
The I/O traffic controller is the module that monitors the status of devices. There is a device handler for every I/O device and they are housed in different processes connected to the device.
The I/O subsystem consists of –
- The part of the memory management component that includes buffering, caching, and spooling.
- A general device driver interface. Drivers for specific hardware devices.
We can manage the I/O system using these all system process techniques. They are :
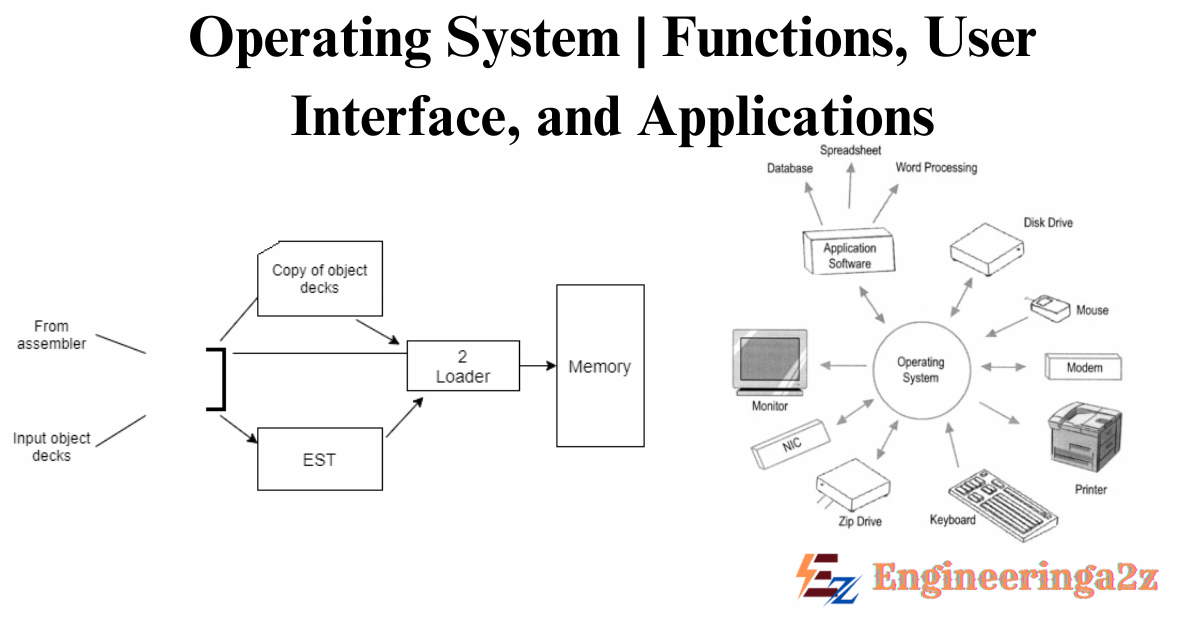
Assembler
Assembler is an assembly language program. An object program and the data needed for the loader to get the object program ready for execution make up output. The computer programmer used to have access to a simple machine that could translate some basic instructions into hardware. He would write a string of ones and zeros (machine language) and input them into the computer memory to program it.
Compiler
Compilers and interpreters handle the high-level languages, of which FORTRAN, COBOL, ALGOL and PL/I are examples. Compiler is software that reads a source program written in a high-level language and generates an object program that matches it. A program that simulates the execution of a source program as if it were machine language is called an interpreter . It is common to refer to a compiler and the language it is associated with by the same name (FORTRAN, COBOL, etc.).
Loader
An object program is loaded and ready for execution by a loader, which is a routine. There are three different loading strategies: Direct Linking, Relocating and Absolute. The loader general tasks include loading, moving and linking the object program. Programs that load into memory and get ready to run are known as loaders. Loader is installed in the core of a basic loading scheme, involving the assembler outputs the machine language translation of an instruction on a secondary device. The user program machine language version is loaded into memory by the loader. Because the loader program is significantly smaller than the assembler and thus makes more core available to the user’s program, it transfers control to it.
Batch System
Some computer systems only did one thing at a time. They had a list of the computer systems that may be dedicated to a single program until its completion or they may be dynamically reassigned among a collection of active programs in different stages of execution.
Batch operating system is one where programs and data are collected together in a batch before processing starts. A job is a predefined sequence of commands, programs and data that are combined into a single unit called a job.
Scheduling is also simple in a batch system. Jobs are processed in the order of submission, i.e. first come, first served fashion.
Advantages of Batch System
- Move much of the operator’s work to the computer.
- Increased performance since the job could start as soon as the previous job finished.
Disadvantages of the Batch System
- Turnaround times can be lengthy for users.
- Programme is difficult to debug.
- An unending cycle could occur in a job. A job could contaminate the monitor, which would impact open jobs.
- One batch job may have an impact on pending jobs since there is no protection scheme in place.
Applications of Operating System
Programs and their users can access services from an operating system. It offers a single setting in which applications can be run . There is a difference in the difficulty of services offered by different operating systems. Programming is made easier by the operating system.
Here are important services provided by operating system they are :
1. Program execution : The operating system potential to load a program into memory and manage the program. The program must be able to end its execution, either normally or abnormally.
2. I/O Operation : Input/output operation refers to the process used to choose the directive in which I/O processes are submitted to storage volumes.
3. File system manipulation : In file system manipulation means read and write programs executed in the operating system.
4. Communication : Data transfer between two components which are threads, process and device drivers.
5. Error detection : Error detection means os has a responsibility to prevent the resources with errors These errors are hardware errors or software errors. If any error occurs during the process the error is displayed on a blue screen what type of errors occur during the process and how to fix those errors are also displayed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Define operating system?
Operating System is an interface between the user and Kernal. An operating system serves as a bridge or interface between a computer’s user and its hardware.
-
Explain various functions of the operating system?
The operating system manages the process of program executions, manages the process and controls the device drivers or peripherals
-
Explain I/O system management?
I/O is a functionality of an operating system which means it handles the input and output operations of your device or computer.
Related Posts
- BTech Computer Science Engineering Previous Years Question Papers PDF
- PLC and Microcontroller Notes PDF (Handwritten)
- Organizational Computational Models
- Processes and Threads in Operating System
- Internet of Things | Functional Block of IoT, Characteristics and Application
- SCADA | Types, Block Diagram and Functions of SCADA System













Leave a Reply