Table of Contents
Introduction
Power quality refers to how close the electrical voltage is to its ideal state at any given time. High-quality voltage appears as a smooth sine wave with the expected voltage and frequency. An ideal electrical source delivers energy without any fluctuations in voltage. Power companies were often blamed for power quality issues in the past, but many factors affecting power quality are beyond their control.
Historically, power quality problems were mainly caused by issues in power distribution, such as lightning, line failures, or high electrical demands. However, in recent times, most power quality problems arise from changes in technology and how people use electricity.
As technology evolves, manufacturers of Power Conditioning and Power Quality equipment face new challenges. The goal is to ensure that new technology doesn’t negatively impact older systems and cause electrical problems. The constant improvement and cost reduction of equipment can lead to power quality issues, prompting critical power protection systems to adapt and change their technology to cope with these challenges.
Sources Of Pollution In Power Quality
Power quality pollution can arise from various sources and factors. Here are some common sources of power quality issues:
- Harmonics: Harmonics are unwanted frequencies that result from non-linear loads like computers, electronic devices, and variable speed drives. These harmonics can distort the voltage and current waveforms, leading to power quality problems.
- Voltage Fluctuations: Voltage fluctuations can occur due to sudden changes in load, equipment starting and stopping, or grid-switching operations. These fluctuations can affect the performance of sensitive equipment and cause disruptions.
- Voltage Surges/Spikes: Voltage surges or spikes happen due to lightning strikes, switching operations, or sudden disconnection of large loads. They can lead to equipment damage and failures.
- Voltage Dips/Sags: Voltage dips or sags occur when there is a temporary drop in voltage levels. They can happen due to faults in the power distribution system or the starting of large motors. These dips can disrupt the operation of equipment and devices.
- Frequency Variations: Frequency variations can occur due to changes in the generation or transmission of electricity. Equipment designed for a specific frequency may not function properly under different frequencies.
- Transient Voltage: Transients are short-duration voltage fluctuations caused by lightning, switching operations, or faults. They can damage electronic devices and sensitive equipment.
- Power Factor: A low power factor occurs when the ratio of real power to apparent power is low. It can lead to inefficient energy usage and increased losses in the power system.
- Imbalance in Load: Uneven distribution of load across the phases of a three-phase power system can result in load imbalance, leading to voltage and current imbalances.
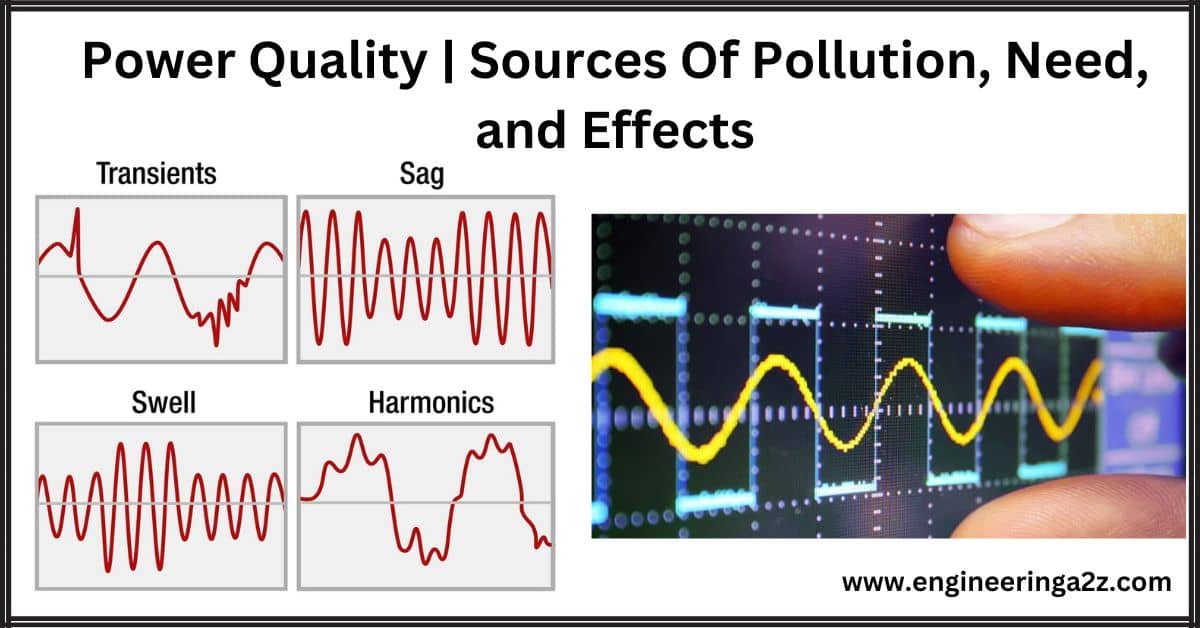
Voltage Quality Disturbances
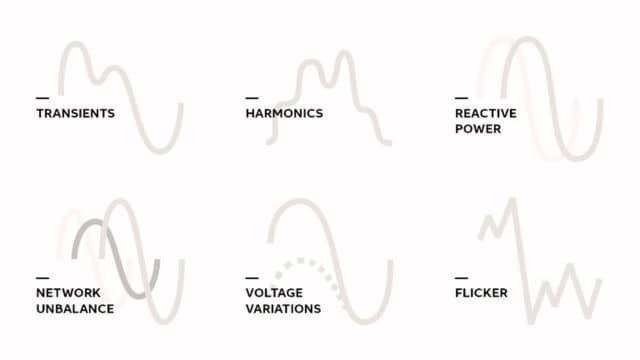
Power quality disturbances are unwanted variations in the electrical power supply that can negatively impact the performance and reliability of electrical and electronic equipment. These disturbances can occur due to various factors and can lead to a range of problems. Some common power quality disturbances include:
- Voltage Sag (or Dip): A voltage sag is a temporary decrease in voltage levels, usually caused by sudden changes in load or faults in the power system. It can disrupt the operation of sensitive equipment, leading to malfunctions or shutdowns.
- Voltage Swell: A voltage swell is a temporary increase in voltage levels, often caused by sudden load reductions or capacitor switching. It can cause stress on electrical equipment, potentially leading to damage.
- Voltage Interruption: A voltage interruption is a complete loss of voltage, which can occur due to faults, lightning strikes, or equipment failures. It results in a sudden and complete loss of power.
- Voltage Fluctuations: Voltage fluctuations are rapid changes in voltage levels, typically caused by varying loads or switching operations. They can lead to flickering lights and affect the performance of sensitive devices.
- Harmonics: Harmonics are unwanted frequencies that can distort the voltage and current waveforms. They are often caused by non-linear loads like computers, electronic devices, and variable speed drives, leading to overheating of equipment and interference with communication systems.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): EMI occurs when electromagnetic signals from electronic devices interfere with other nearby electrical systems, causing disruptions and malfunctions.
- Frequency Variations: Frequency variations can result from imbalances in the power grid or generator speed fluctuations. They can affect time-sensitive equipment and motor-driven systems.
- Transients (Surges and Spikes): Transients are sudden, short-duration voltage increases (spikes) or decreases (surges). They can be caused by lightning strikes, capacitor switching, or other events, potentially damaging sensitive electronics.
- Unbalanced Voltages and Currents: Unbalanced voltages and currents occur when the three phases of a three-phase power system have unequal values. It can lead to overheating of motors and inefficiencies in power transmission.
- Voltage Flicker: Voltage flicker is a rapid variation in voltage, often caused by fluctuating loads and can be visually observed as varying brightness in lighting.
Managing power quality disturbances is essential to ensure the reliable operation of electrical equipment, prevent damage, and reduce downtime. This can be achieved through proper power system design, the use of power quality mitigation devices, and regular maintenance of electrical systems.
Need For Power Quality
In the emerging surplus power scenario, the characteristics of loads and the requirements of electrical systems have changed significantly. The devices and equipment used presently in industrial, commercial, and domestic facilities are more sensitive to supply variations than equipment used in the past. This is due to the increased use of power electronics and microprocessor-based technologies in equipment and appliances. The increasing penetration of Renewable sources of energy, semiconductor-based electronic equipment, non-linear loads, data centers, industries running on adjustable speed drives and arc furnaces, etc. distort voltage/current waveforms in non-conformity to their desired form. This brings challenges to maintaining the quality of power to the ideal one and ensuring efficacy.
In India, various sectors are prone to both generations of higher power quality pollution as well as susceptibility to power quality disturbances. The losses due to power quality issues are economic as well as technical. Both utilities as well as consumers are heavily impacted due to the techno-economic losses arising out of poor power quality. Poor power quality not only causes performance degradation and premature failure of electrical equipment but also results in increased system losses, financial loss, etc. Therefore, apart from the reliability i.e. continuous supply, the preference of the electricity consumers is shifting towards quality power supply from the distribution licensees. Optimum power quality can enhance productivity and reduce losses.
Effect Of Poor Power Quality
Power quality is a significant issue that needs attention because it can lead to financial losses and downtime. Let’s look at some direct and indirect costs associated with power quality problems.
Direct costs are related to the loss of production when voltage issues cause motors and control devices to trip, halting the manufacturing process. This results in products not being produced and additional expenses for removing damaged materials and paying employee wages while waiting for the process to restart.
Indirect costs involve replacing equipment that gets strained by fluctuating electrical voltages. For example, a solid-state motor drive may fail due to voltage spikes over time, often caused by power factor capacitors switching on and off to correct varying power factors. The damage to the machine accumulates gradually from multiple spikes over time, making it difficult to prevent the outage from happening. This can result in unexpected downtime and costly repairs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the 4 causes of poor power quality?
However, the most common causes can be broken down into four distinct areas: harmonic pollution, low power factor, load imbalances, and voltage variations.
What are power quality disturbances?
In simple terms, a power quality disturbance is any unexpected change in the electricity (voltage, current, or frequency) that disrupts the proper functioning of electrical devices and equipment. These disturbances can cause issues like flickering lights, equipment malfunction, or even damage to electronic devices. So, ensuring good power quality is important to avoid such disruptions and keep our electrical systems running smoothly.
What are disturbances in a system?
Noise and disturbance are unwanted signals that interfere with the desired output or input of a feedback control system. Noise can originate from various sources, such as measurement errors, sensor noise, environmental factors, or random fluctuations.
Read Also:
- Magnetic Field | Introduction | Effects
- Globalisation | Impacts of Globalisation
- Computer Aided Electrical Machine Design Notes
- Biomass Resources | Environmental Impacts, Constituents, and Applications
- Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB) | Types, Working Principle, And Construction




Leave a Reply