Table of Contents
Brayton Cycle
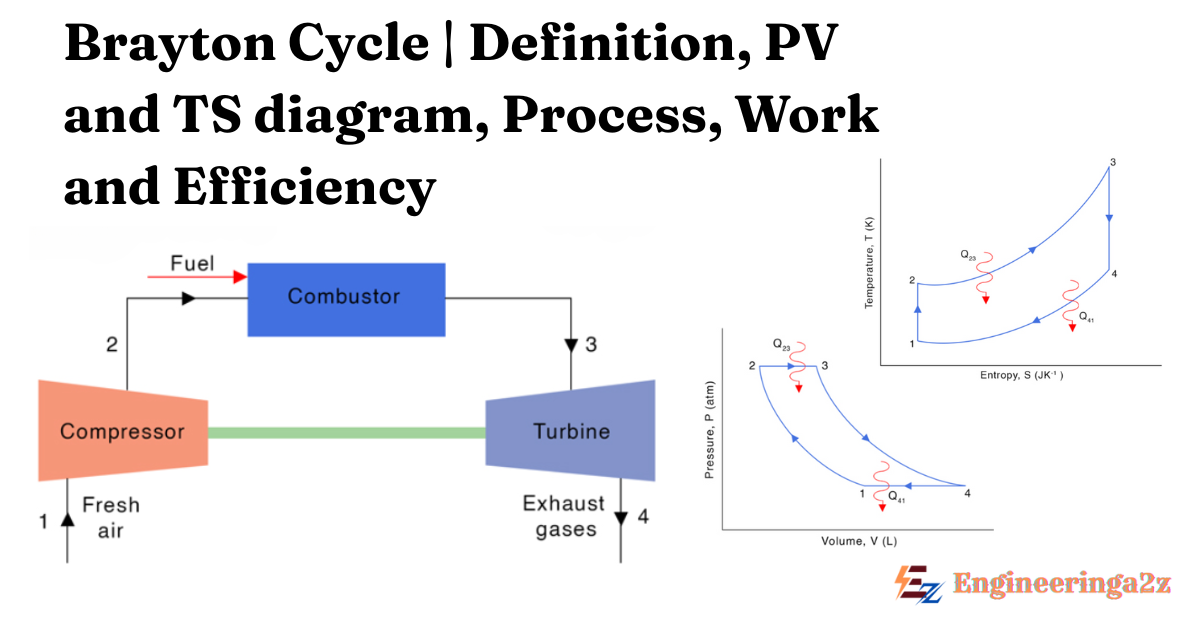
The Brayton cycle, also known as the Joule Cycle. It is a thermodynamic cycle that describes the operation of a gas turbine engine. It is a type of heat engine that generates power by using a combination of compression, heat addition and expansion. The brayton cycle is used in gas turbine engine.
PV and TS Diagram of Brayton Cycle
The ideal Brayton cycle has four processes. PV and TS diagram shown below:
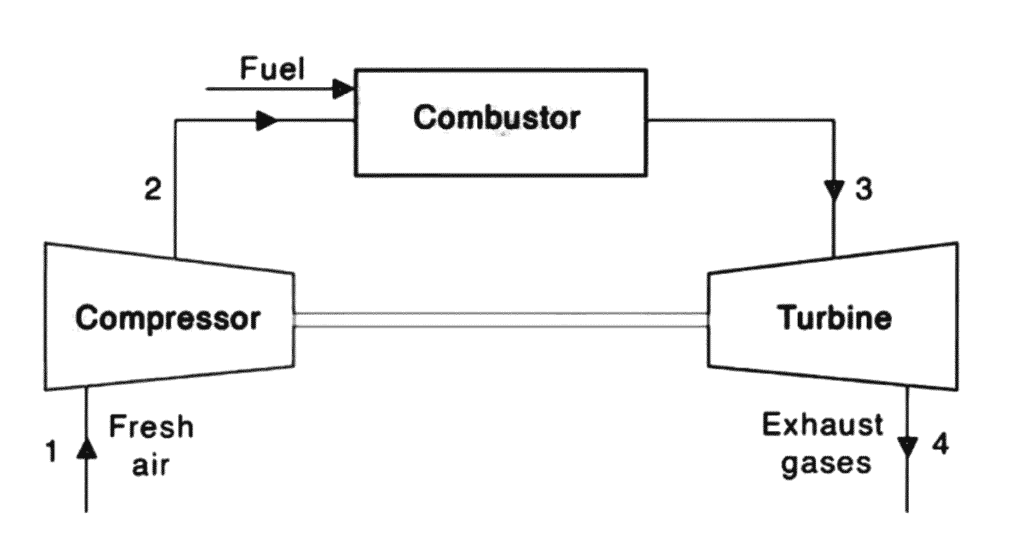
First is PV Diagram,
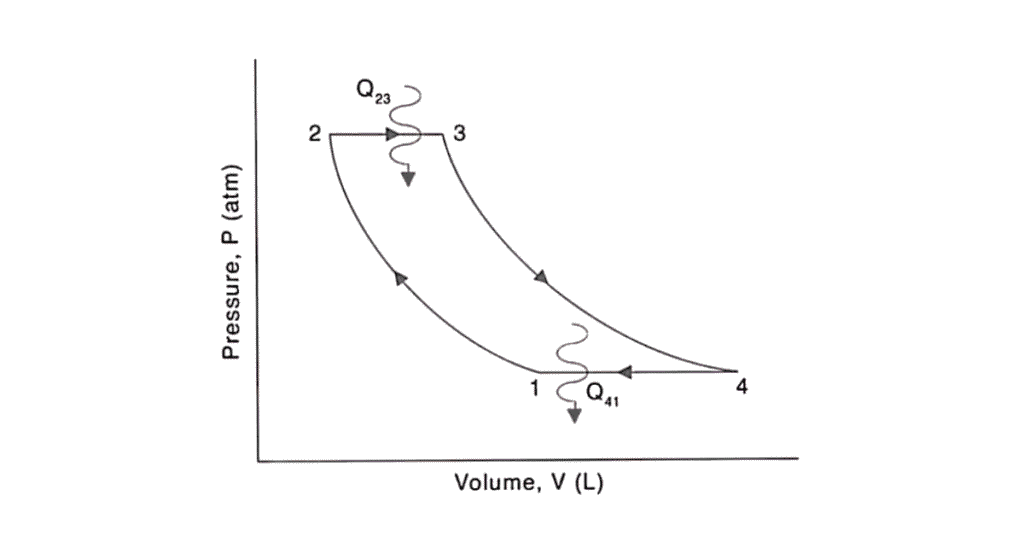
Second is TS Diagram,
Processes of Brayton Cycle
There are four process of ideal bryton cycle:
Process 1 → 2 Isentropic Compression
Compression of air, increasing pressure and temperature. Pressure is compressed from pressure P1 to P2. Volume reduces from V1 to V2 . Temperature increases from T1 to T2. Entropy (S) has remained constant, S1 = S2.
Process 2 → 3 Heat Addition
Heat addition at constant pressure, increasing volume and temperature. Fuel burns at constant pressure, P2 = P3. Temperature rises from T2 to T3, volume expands from V2 to V3 and entropy increases from S2 to S3.
Process 3 → 4 Isentropic Expansion
Expansion of hot gases, decreasing pressure and temperature. Pressure decreases from P3 to P4, temperature decreases from T3 to T4 and volume increases from V3 to V4.
Process 4 → 1 Heat Rejection
Heat rejection at constant pressure, decreasing volume and temperature. Isobaric heat rejection in this process pressure is constant, P4 = P1. Volume decreases from V4 to V1. Gas temperature decreases from T4 to T1 and entropy decreases from S4 to S1.
Work Output and Thermal Efficiency of Brayton Cycle
Here we find the work done, the heat absorbed and the thermal efficiency of the Brayton cycle. Firstly we take the cycle from a -b -c -d and back to a. According to the first law of thermodynamics,

Here change in μ is zero because μ is a state of function. The net work done is,

For a constant pressure, quasi-static process the heat exchange per unit mass is

First law in terms of enthalpy or by remembering the definition of cp .
For the heat addition from the combustor,

Heat rejection is, similarly above equation,

Net work per unit mass is given by

The thermal efficiency of the brayton cycle,

Constant pressure process points are a, b and c and Pa = Pb = Pc . The cycle are adiabatic and reversible,

the thermal efficiency of a Brayton cycle:

The temperature ratio, Tb /Ta = TR. This relation using for an adiabatic reversible process we can write the efficiency in terms of the pressure ratio,

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is the Brayton Cycle Process in Thermodynamics?
Isentropic compression air is compressed, increasing its pressure and temperature. Constant Pressure Heat Addition Fuel is burned, adding heat to the compressed air at constant pressure. Isentropic Expansion: The hot gases expand, producing work and decreasing pressure and temperature. Constant Pressure Heat Rejection Heat is rejected at constant pressure, returning the system to its initial state.
-
What is Brayton Cycle Principle Used in Gas Turbines?
Brayton cycle is the basis of the gas turbine. It is a thermodynamic cycle that describes the operation of a gas turbine engine. It is a type of heat engine that generates power by using a combination of compression, heat addition and expansion. The Brayton cycle is used in gas turbine engine.
Related Posts
- Wind Energy | Engineeringa2z
- What is Electric Heating
- Unified Power Flow Controller | Control, Protection, and Charactersitcs
- Transmission Line | Introduction, Classification, and Modelling
- Total Quality Management | History, Importance, and Characteristics
- Tidal Energy | Working, Parts, and Applications














Leave a Reply