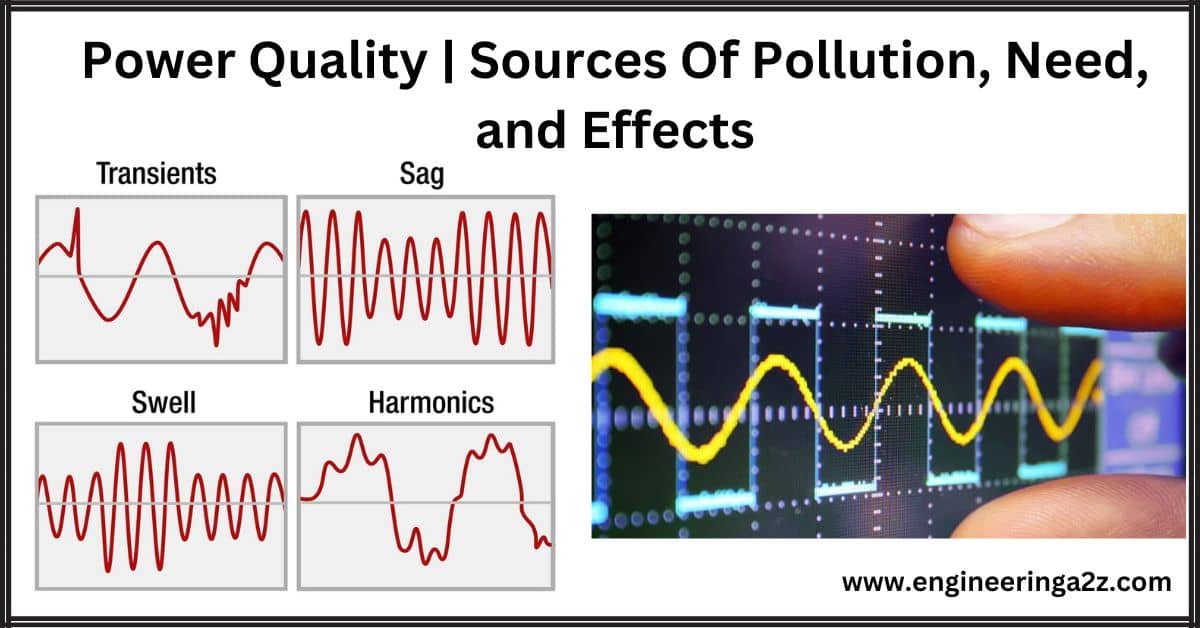
Power Quality | Sources Of Pollution, Need, and Effects
Introduction Power quality refers to how close the electrical voltage is to its ideal state…
Energy Conservation | Principle, Importance and Its Benefits
Introduction Energy conservation means using less energy by being smarter with how we use it.…
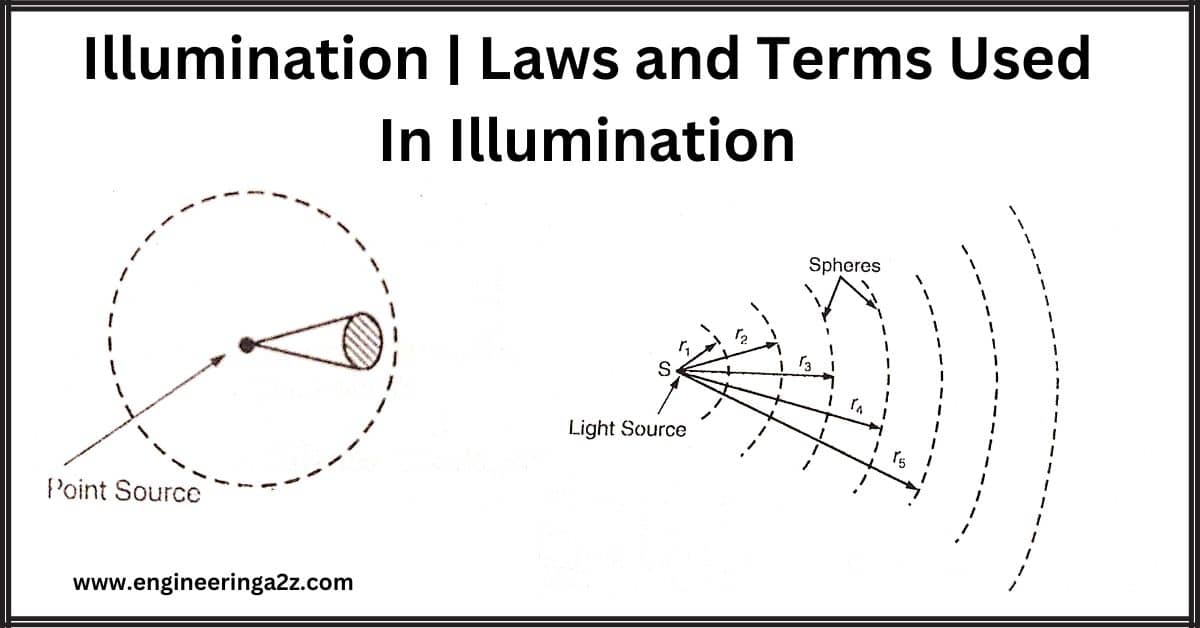
Illumination | Laws and Terms Used In Illumination
Introduction In general, by "Illumination" we mean "lighting". Technically illumination is the light required at…
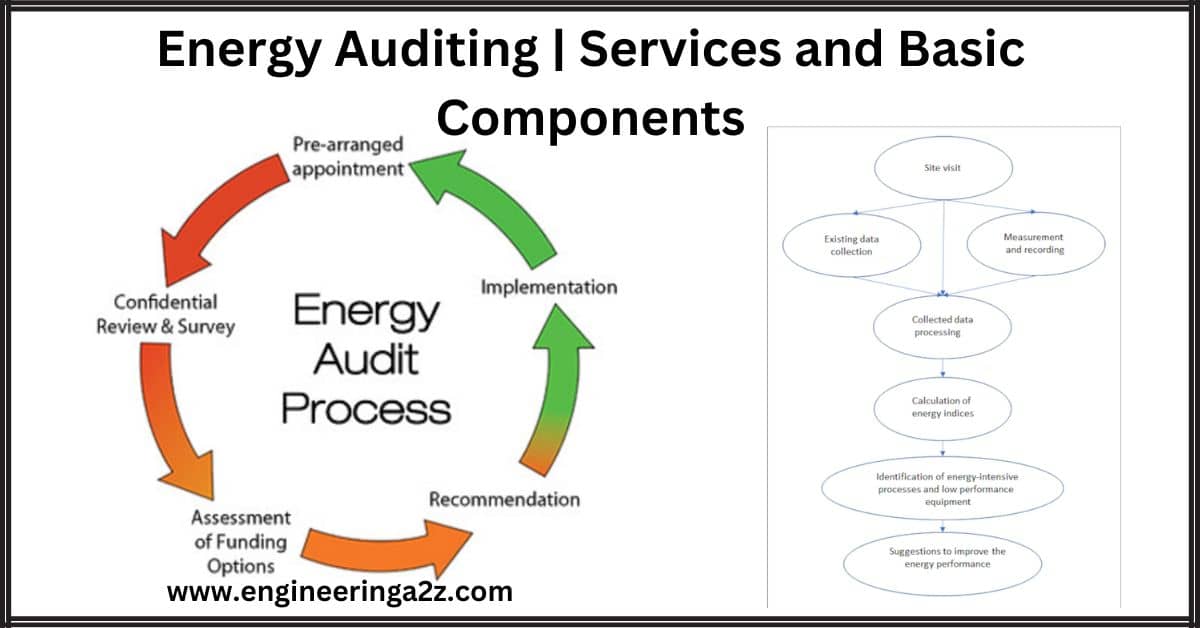
Energy Auditing | Services and Basic Components
Introduction An energy audit is like a thorough check-up for a building to see how…
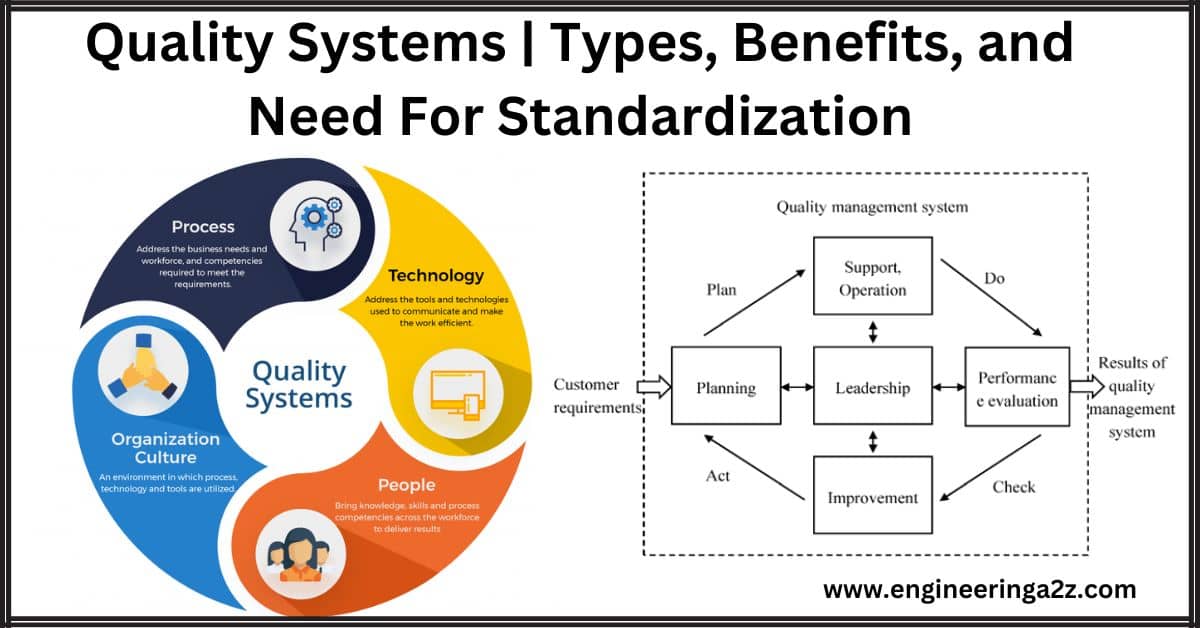
Quality Systems | Types, Benefits, and Need For Standardization
A Quality Management System (QMS) is like a set of organized rules that a company…
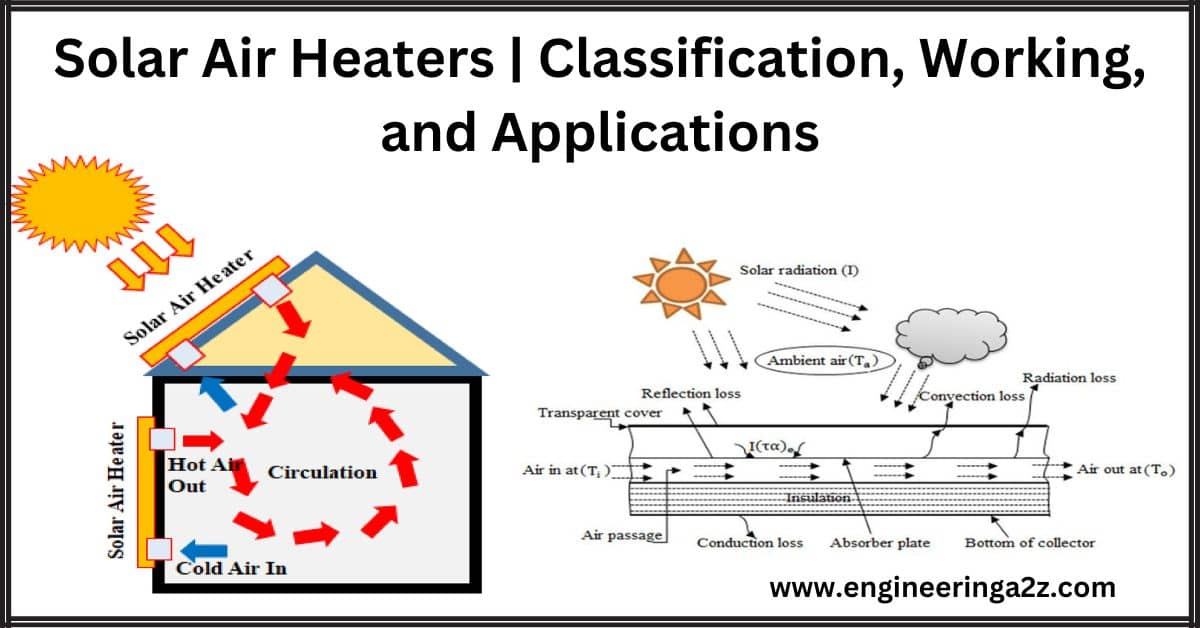
Solar Air Heaters | Classification, Working, and Applications
Solar Air Heaters A solar air heater is a special solar system that uses sunlight…
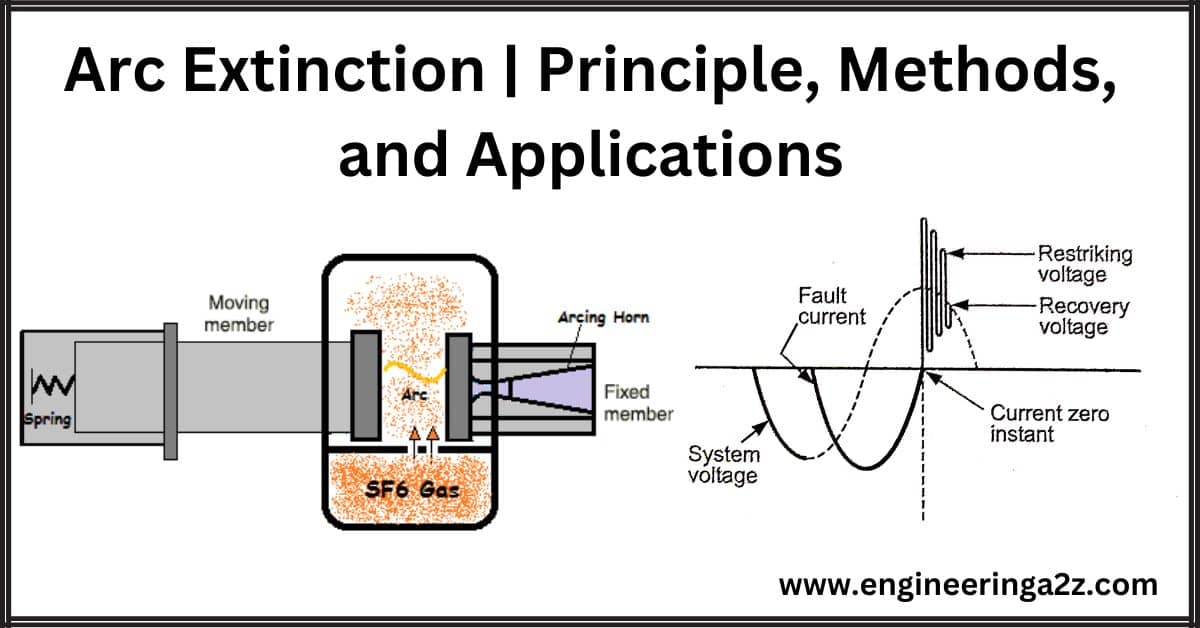
Arc Extinction | Principle, Methods, and Applications
Arc Extinction Arc extinction refers to the process of stopping or extinguishing an electric arc…
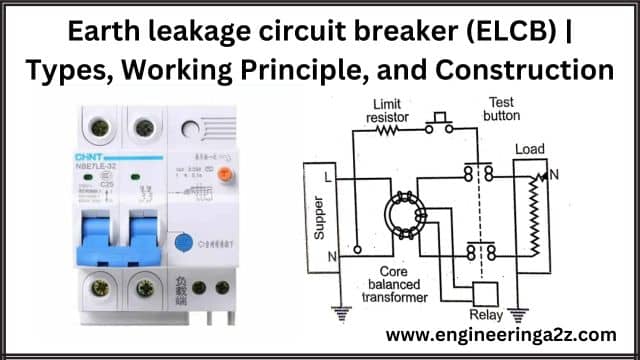
Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB) | Types, Working Principle, And Construction
Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB) In industrial, commercial, and domestic buildings sometimes leakage to earth…
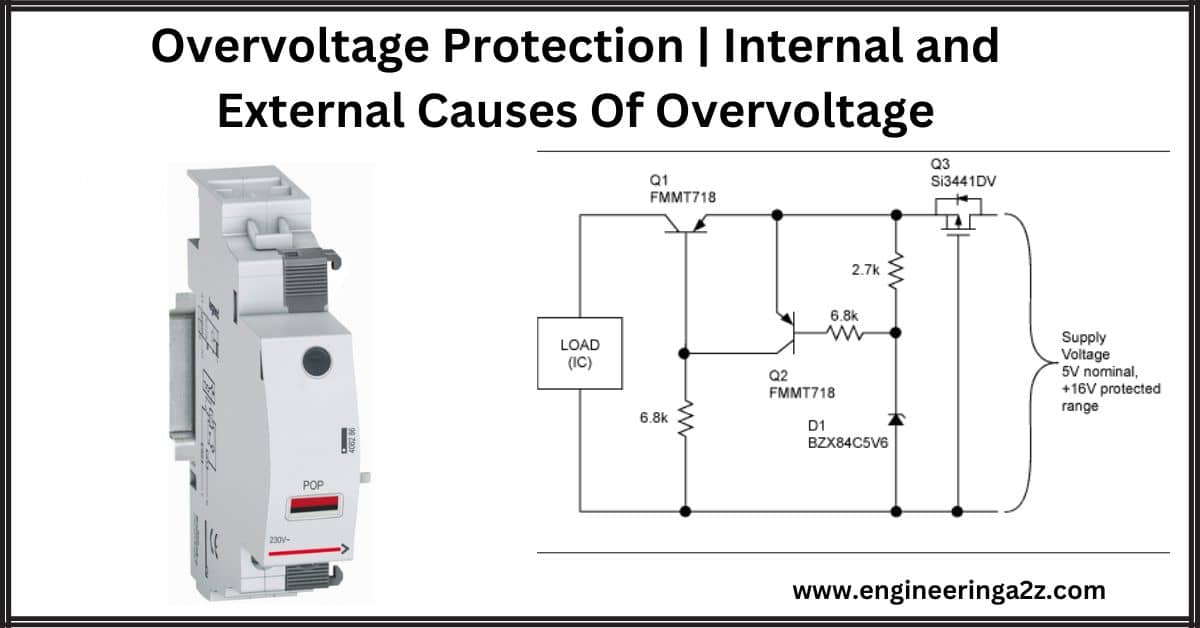
Overvoltage Protection | Internal and External Causes Of Overvoltage
Introduction Voltages more significant than typical voltages are called overvoltages. These may affect the power…









Comments