
Table of Contents
Pulse Code Modulation
Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) is a digital technique used to convert analog signals into digital form. It is one of the most widely used methods in digital communication systems, especially in telephony, audio recording and data transmission.
PCM converts a continuously varying analog signal into a sequence of binary digits (0s and 1s) so that it can be easily stored, processed and transmitted with high reliability.
A pulse code modulation is a digital-to-analog conversion. The PCM comprises four processes :
- PAM Sampling,
- Quantization,
- Binary Encoding,
- Digital to Digital Encoding.
PAM sampling is obtaining a sequence of instantaneous values of the single at regular. Quantization is a long-distance signal. An encoder is a combination of quantization and sampling.
Block Diagram of Pulse Code Modulation

(1) Analog Signal: Any continuous time signal that represents some physical quantity is called an analog signal. An analog signal is continuous in nature and is transmitted in the form of constant waves.
(2) Low Pass Filter: Low pass filter (LPF) is a circuit that only passes a signal below its cutoff frequency while reducing all signals above it.
(3) PAM Sampling: It is the process of obtaining a sequence of instantaneous values of a signal at regular intervals. The output of a sampling circuit is a series of discontinuous values that represent the amplitude of the input signal at specific points in time.
The value of Ts must be:
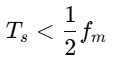
(4) Quantization: At long-distance signals, there are a lot of chances for the introduction of noise. To overcome this noise quantization is used. In quantization, the information signal is modified.
Suppose the information signal m(t) is present before quantization. After quantization, this signal is modified and a new signal mq(t) is generated. The difference between two adjacent samples is called the step size.
The basic function of a quantizer is to convert discrete-time continuous-amplitude signal into a discrete-time discrete-amplitude signal.
(5) Encoder: After sampling and quantization, an encoding process is required to convert the discrete set of sample values into a more suitable form of signal. Normally binary coding techniques are used for encoding.
(6) PCM: A pulse code modulation is a conversion of the analog signal into a digital signal and receive the signal.
Advantages of Pulse Code Modulation
- High Noise Immunity: Digital signals are less affected by noise than analog signals.
- Long-Distance Transmission: Regenerators can clean up the signal, allowing it to travel long distances without significant degradation.
- Easy Encryption: Digital signals can be easily encrypted for secure communication.
- Integration with Digital Systems: PCM signals can be easily processed and stored by computers and other digital devices.
Disadvantages of Pulse Code Modulation
- PCM systems suffer from disadvantages like the complex method of encoding, decoding, and quantization.
- In PCM system requires a large bandwidth as compared to other systems.
- A large bandwidth is required for transmission.
- Noise and crosstalk live but rise attenuation.
Applications of Pulse Code Modulation
- Telecommunications: Used in digital telephone networks to convert voice signals into digital signals for transmission.
- Audio Recording: Used in CDs, DVDs and digital audio workstations (DAWs) to record and store high-quality audio.
- Video Recording: Used in digital video cameras and recorders to capture and store video.
- Digital Radio: Used in digital audio broadcasting (DAB) systems to transmit radio signals digitally.
- Medical Imaging: Used in medical imaging devices like MRI and CT scanners to convert analog signals from sensors into digital images.
- Satellite Communication: Used for transmitting data from satellites to ground stations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is the full form of PCM?
PCM stands for Pulse Code Modulation.
-
What is an analog signal in PCM?
An analog signal is a continuous-time signal that represents a physical quantity such as sound, temperature or pressure.
-
What is a Low Pass Filter?
A low pass filter (LPF) is a circuit that only passes a signal below its cutoff frequency while attenuating all signals above it.
-
What are the advantages of PCM?
1. PCM signals can be easily stored and processed due to their digital nature.
2. PCM systems are highly immune to channel noise.
3. Signal regeneration at the receiver is simple and reliable.
4. PCM provides better signal quality compared to analog transmission.
Related Posts
- Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT): Types, Working, Construction, Advantages
- MOSFET | Working Principle | V-I Characteristics & Applications
- Full Wave Rectifier | Definition, Types and Working
- Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO) Construction and Working Principle
- Solar Cell or Photovoltaic Cell Construction and Working
- B.Tech – Electrical Engineering Previous Year Question Papers Download














Leave a Reply