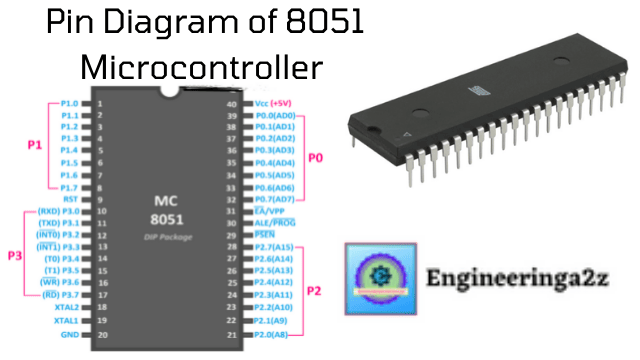
Pin Diagram of 8051 Microcontroller
Pin Diagram of 8051 The 8051 microcontroller has 40 pins of dual-in-line packaging and is…
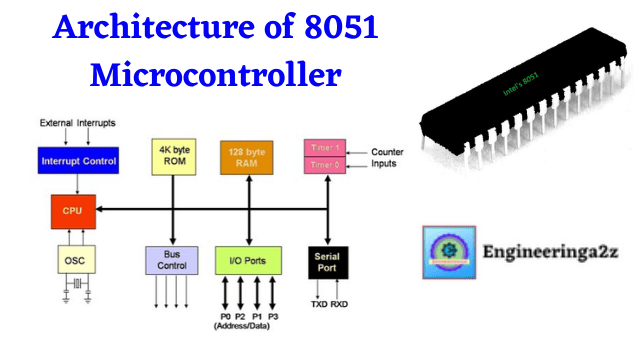
Architecture of 8051 Microcontroller
Architecture of 8051 Basic components present internally inside 8051 microcontroller architecture are: CPU (Central Processing…
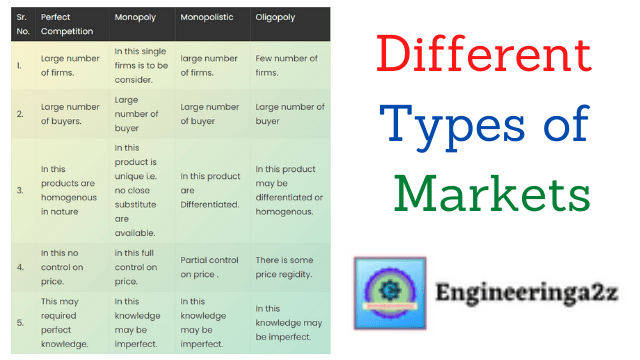
Markets: Perfect competition, Monopoly, Monopolistic & Oligopoly
Economics For Engineers Book PDF : Economics for engineers book by T.R. Jain. Sr. No.Perfect…
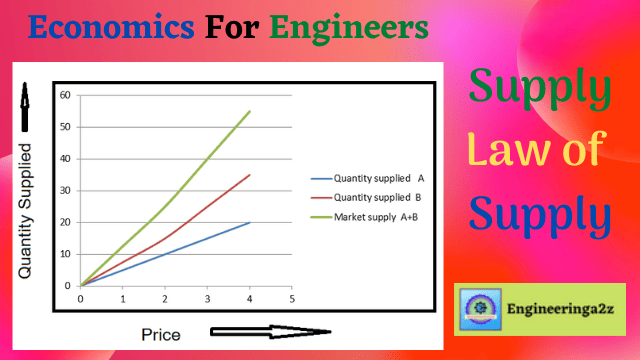
Supply : Law of Supply
What is Supply? Supply is a quantity of a commodity that a producer is willing…
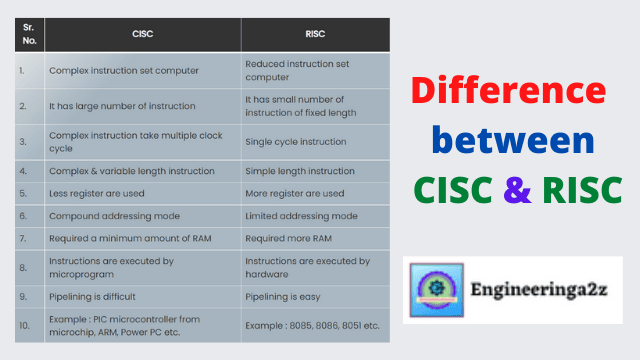
Difference between CISC & RISC
CISC :- CISC stands for complex instruction set computer. RISC :- RISC stands for reduced…
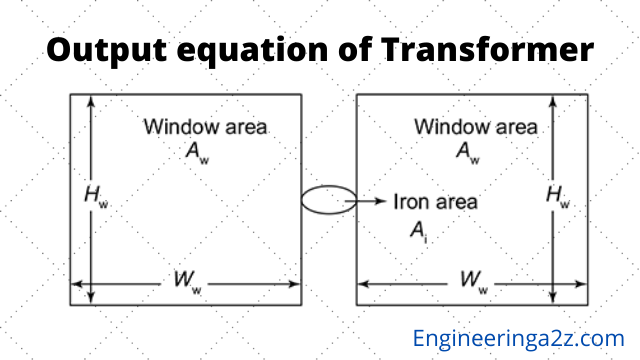
Output Equation of Transformer
Output Equation The output equation of transformer in KVA is to be related with its…
Difference between Microprocessor & Microcontroller
Sr. No.MicroprocessorMicrocontroller1.A microprocessor is a general purpose device which is called CPU. A microcontroller is…
Globalisation | Impacts of Globalisation
Introduction of Globalisation Globalisation simply means that combining the economy of the country with the…
Main Components of Overhead Lines
You may also like List of the main components of an overhead line Support:- Depending on…
Basic Electrical Engineering (BEE) | Engineeringa2z
What is electrical engineering? Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design…











Comments