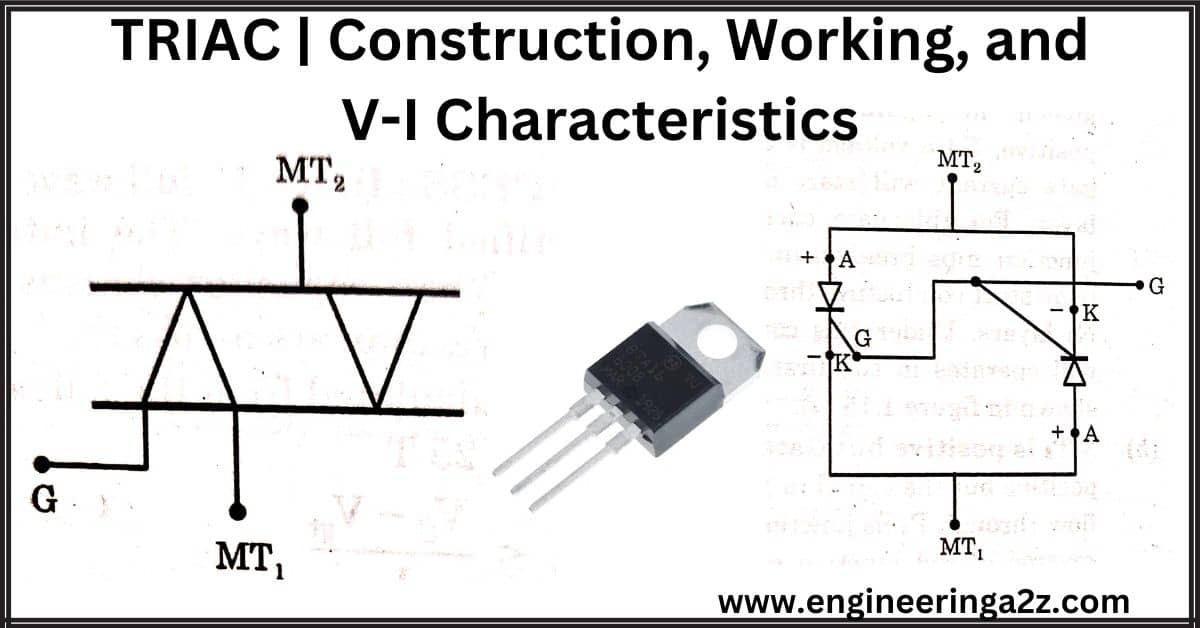
TRIAC | Construction, Working and V-I Characteristics
TRIAC An SCR can be conducted in only one direction. So only the positive half…
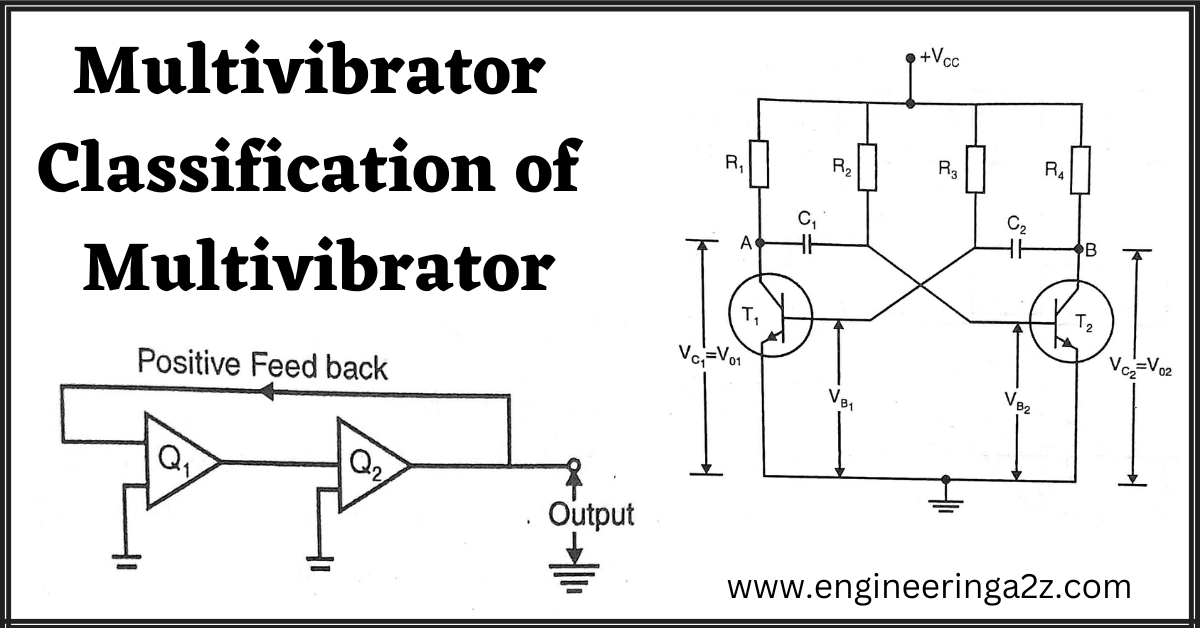
Multivibrator | Classification of Multivibrator
Introduction to Multivibrator Multivibrator is wave shaping circuit which generates non sinusoidal waves called Multivibrator.…
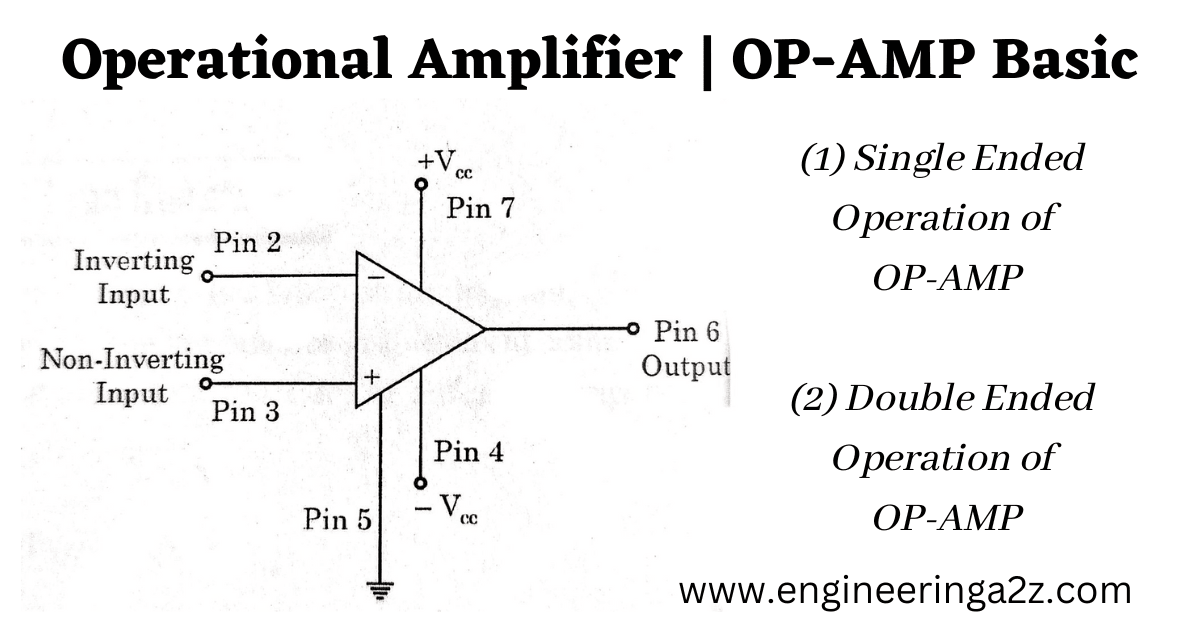
Operational Amplifier | OP-AMP Basic
Introduction An operational amplifier (OP-AMP) is a very stable amplifier that can be used for…
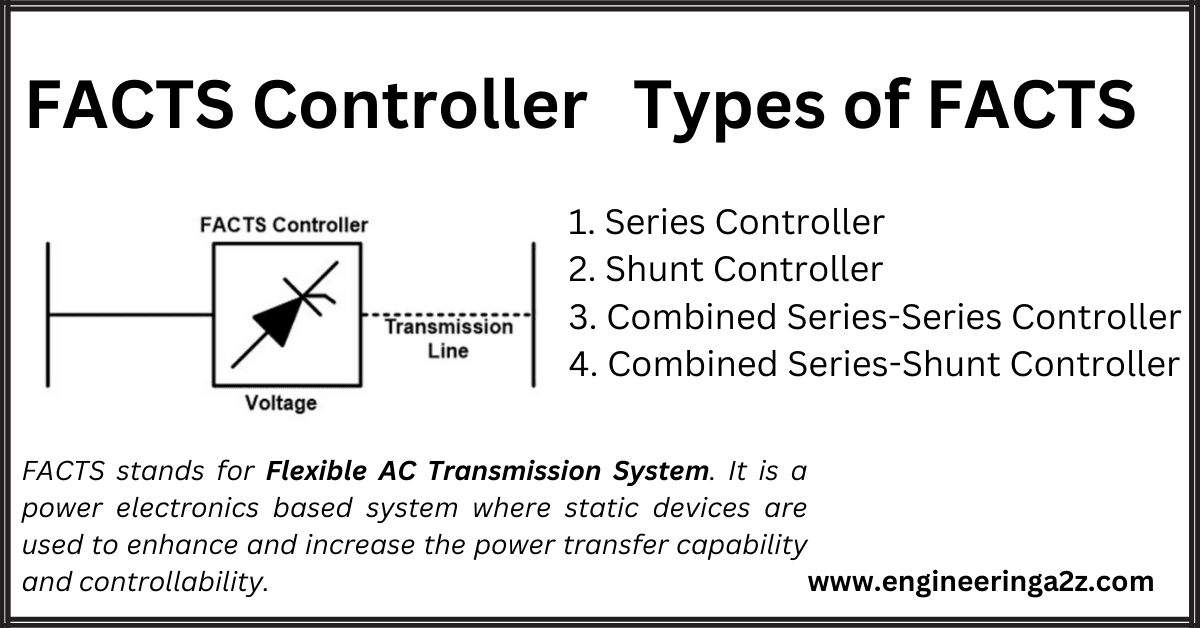
FACTS Controller | Types of FACTS Controller
FACTS FACTS stands for Flexible AC Transmission System. It is a power electronics-based system where…
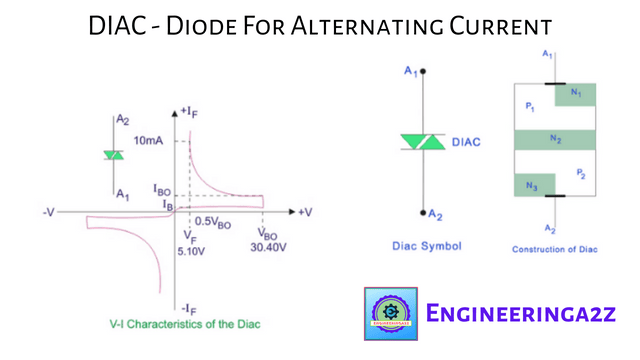
DIAC | Diode for Alternating Current
Introduction of DIAC DIAC simply stated as "Direct for alternating current". A DIAC is a…
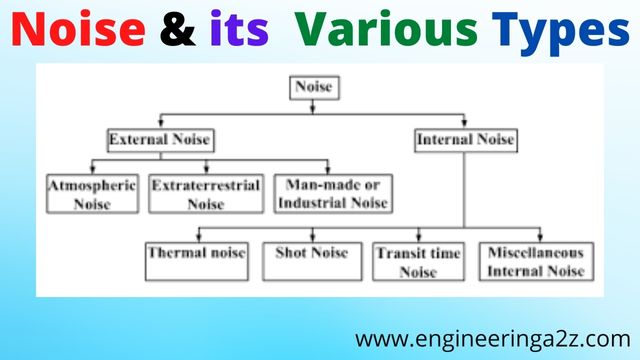
Noise | Noise in Electronics System
Definition of Noise In electrical terms, noise may be defined as an unwanted form of…
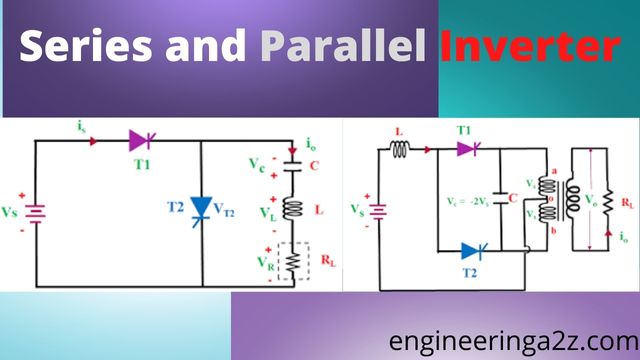
Inverter | Series and Parallel Inverter
Inverter Inverter is a static electrical device which is used to convert DC power into…
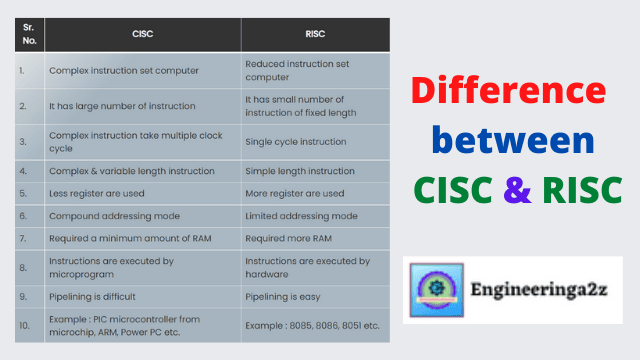
Difference between CISC & RISC
CISC :- CISC stands for complex instruction set computer. RISC :- RISC stands for reduced…
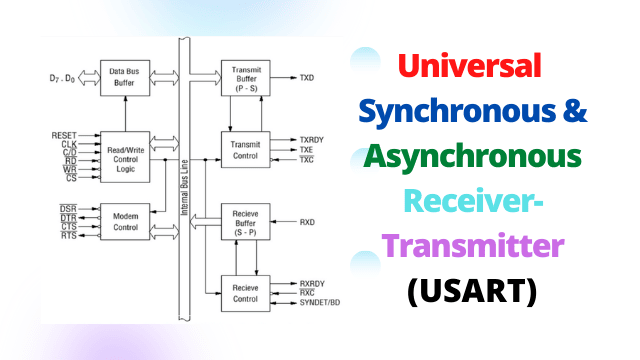
USART (8251) : Universal Synchronous And Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter
Universal Synchronous and Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter (USART) A universal synchronous & asynchronous receiver-transmitter (USART) is a…








Comments